| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
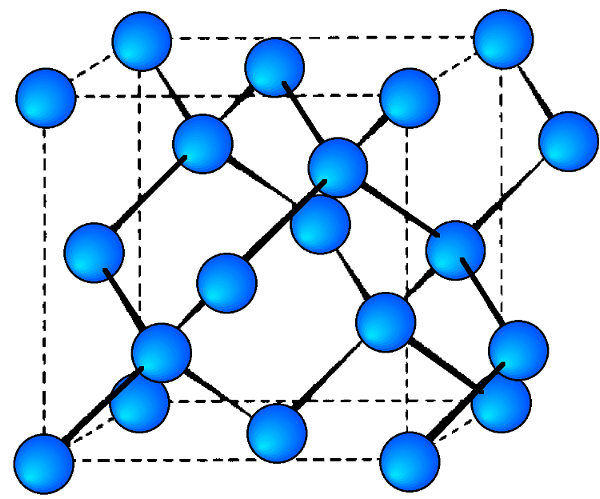
The diamond cubic structure consists of two interpenetrating face-centered cubic lattices, with one offset 1 / 4 of a cube along the cube diagonal. It may also be described as face centered cubic lattice in which half of the tetrahedral sites are filled while all the octahedral sites remain vacant. The diamond cubic unit cell is shown in [link] . Each of the atoms (e.g., C) is four coordinate, and the shortest interatomic distance (C-C) may be determined from the unit cell parameter ( a ).
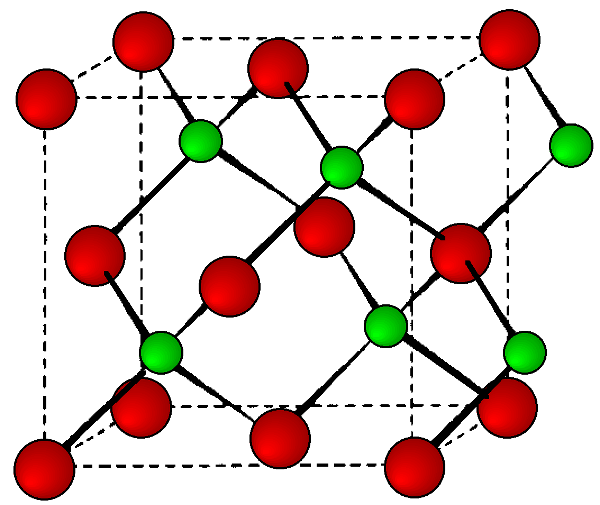
This is a binary phase (ME) and is named after its archetype, a common mineral form of zinc sulfide (ZnS). As with the diamond lattice, zinc blende consists of the two interpenetrating fcc lattices. However, in zinc blende one lattice consists of one of the types of atoms (Zn in ZnS), and the other lattice is of the second type of atom (S in ZnS). It may also be described as face centered cubic lattice of S atoms in which half of the tetrahedral sites are filled with Zn atoms. All the atoms in a zinc blende structure are 4-coordinate. The zinc blende unit cell is shown in [link] . A number of inter-atomic distances may be calculated for any material with a zinc blende unit cell using the lattice parameter ( a ).
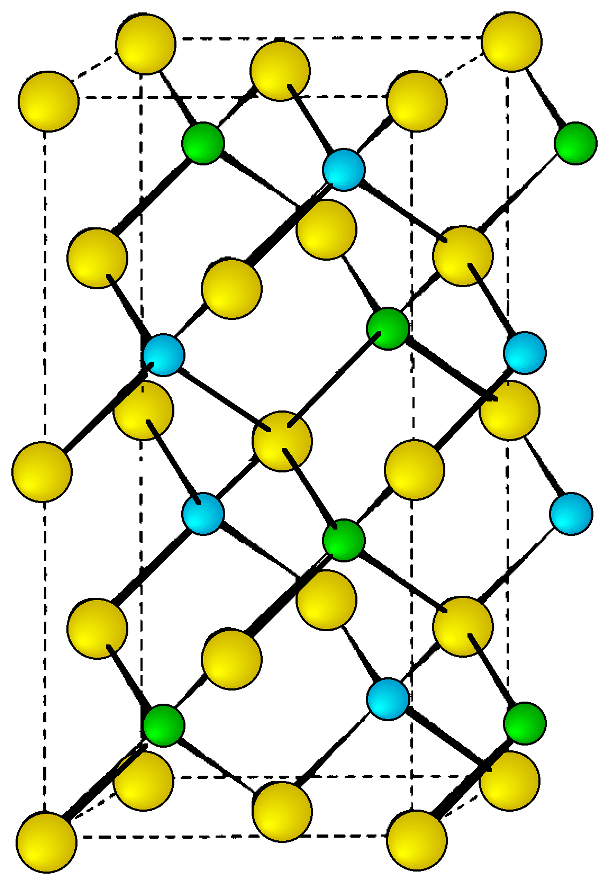
The mineral chalcopyrite CuFeS 2 is the archetype of this structure. The structure is tetragonal ( a = b ≠ c , α = β = = 90°, and is essentially a superlattice on that of zinc blende. Thus, is easiest to imagine that the chalcopyrite lattice is made-up of a lattice of sulfur atoms in which the tetrahedral sites are filled in layers, ...FeCuCuFe..., etc. ( [link] ). In such an idealized structure c = 2 a , however, this is not true of all materials with chalcopyrite structures.
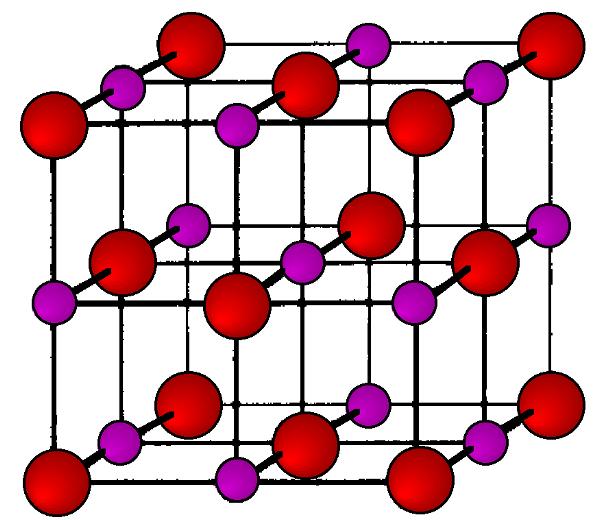
As its name implies the archetypal rock salt structure is NaCl (table salt). In common with the zinc blende structure, rock salt consists of two interpenetrating face-centered cubic lattices. However, the second lattice is offset 1/2 a along the unit cell axis. It may also be described as face centered cubic lattice in which all of the octahedral sites are filled, while all the tetrahedral sites remain vacant, and thus each of the atoms in the rock salt structure are 6-coordinate. The rock salt unit cell is shown in [link] . A number of inter-atomic distances may be calculated for any material with a rock salt structure using the lattice parameter ( a ).
Cinnabar, named after the archetype mercury sulfide, HgS, is a distorted rock salt structure in which the resulting cell is rhombohedral (trigonal) with each atom having a coordination number of six.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of electronic materials' conversation and receive update notifications?