| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This is a hexagonal form of the zinc sulfide. It is identical in the number of and types of atoms, but it is built from two interpenetrating hcp lattices as opposed to the fcc lattices in zinc blende. As with zinc blende all the atoms in a wurtzite structure are 4-coordinate. The wurtzite unit cell is shown in [link] . A number of inter atomic distances may be calculated for any material with a wurtzite cell using the lattice parameter ( a ).
However, it should be noted that these formulae do not necessarily apply when the ratio a / c is different from the ideal value of 1.632.
The cesium chloride structure is found in materials with large cations and relatively small anions. It has a simple (primitive) cubic cell ( [link] ) with a chloride ion at the corners of the cube and the cesium ion at the body center. The coordination numbers of both Cs + and Cl - , with the inner atomic distances determined from the cell lattice constant ( a ).
The room temperature allotrope of tin is β-tin or white tin. It has a tetragonal structure, in which each tin atom has four nearest neighbors (Sn-Sn = 3.016 Å) arranged in a very flattened tetrahedron, and two next nearest neighbors (Sn-Sn = 3.175 Å). The overall structure of β-tin consists of fused hexagons, each being linked to its neighbor via a four-membered Sn 4 ring.
Up to this point we have only been concerned with ideal structures for crystalline solids in which each atom occupies a designated point in the crystal lattice. Unfortunately, defects ordinarily exist in equilibrium between the crystal lattice and its environment. These defects are of two general types: point defects and extended defects. As their names imply, point defects are associated with a single crystal lattice site, while extended defects occur over a greater range.
Point defects have a significant effect on the properties of a semiconductor, so it is important to understand the classes of point defects and the characteristics of each type. [link] summarizes various classes of native point defects, however, they may be divided into two general classes; defects with the wrong number of atoms (deficiency or surplus) and defects where the identity of the atoms is incorrect.
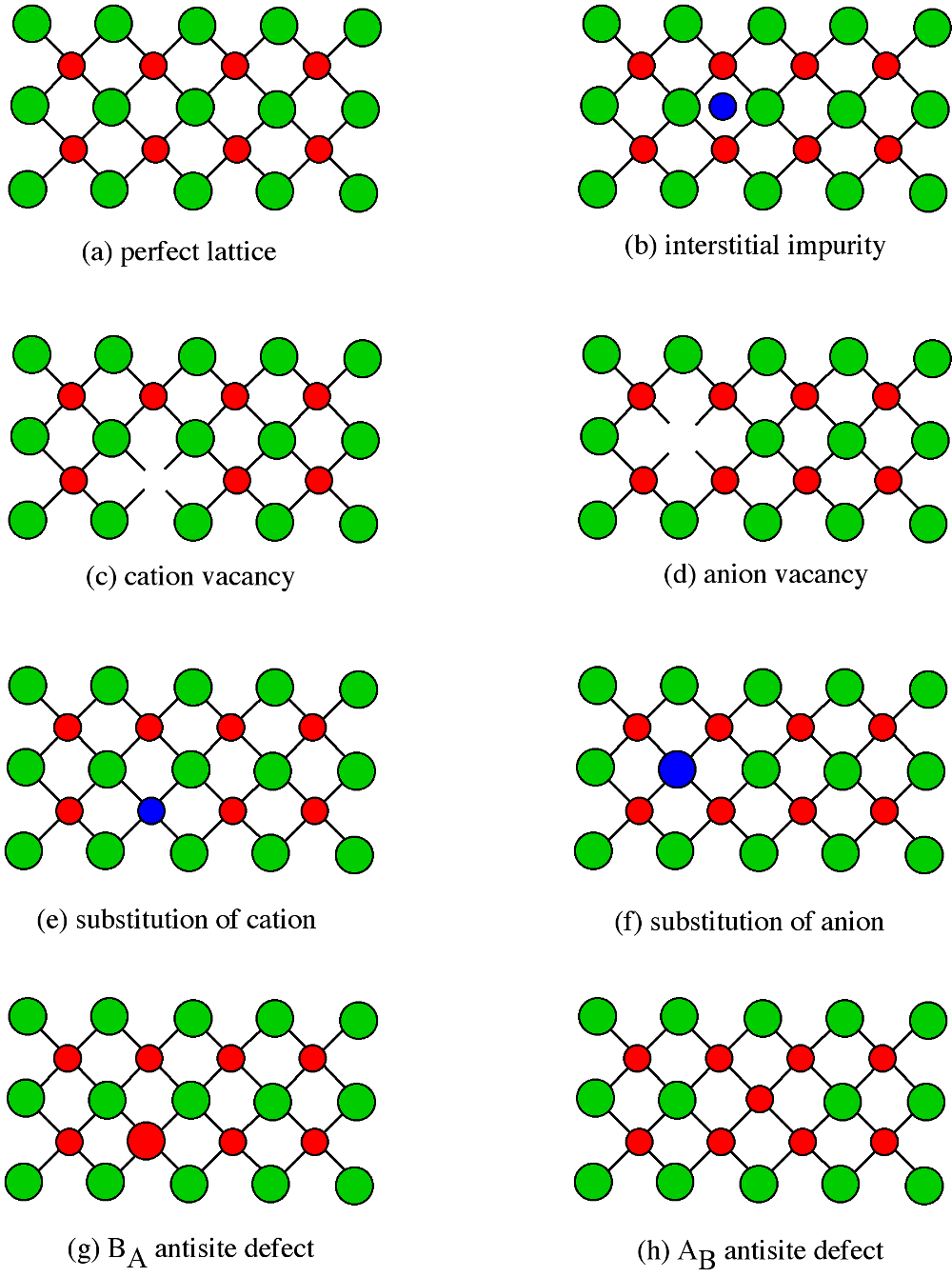
An interstitial impurity occurs when an extra atom is positioned in a lattice site that should be vacant in an ideal structure ( [link] b). Since all the adjacent lattice sites are filled the additional atom will have to squeeze itself into the interstitial site, resulting in distortion of the lattice and alteration in the local electronic behavior of the structure. Small atoms, such as carbon, will prefer to occupy these interstitial sites. Interstitial impurities readily diffuse through the lattice via interstitial diffusion, which can result in a change of the properties of a material as a function of time. Oxygen impurities in silicon generally are located as interstitials.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?