| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A hyperbola is the strangest-looking shape in this section. It looks sort of like two back-to-back parabolas. However, those shapes are not exactly parabolas, and the differences are very important.
Surprisingly, the definition and formula for a hyperbola are very similar to those of an ellipse.
The entire definition is identical to the definition of an ellipse, with one critical change: the word “plus” has been changed to “minus.”
One use of hyperbolas comes directly from this definition. Suppose two people hear the same noise, but one hears it ten seconds earlier than the first one. This is roughly enough time for sound to travel 2 miles. So where did the sound originate? Somewhere 2 miles closer to the first observer than the second. This places it somewhere on a hyperbola: the set of all points such that the distance to the second point, minus the distance to the first, is 2.
Another use is astronomical. Suppose a comet is zooming from outer space into our solar system, passing near (but not colliding with) the sun. What path will the comet make? The answer turns out to depend on the comet’s speed.
 |
 |
| If the comet’s speed is low, it will be trapped by the sun’s gravitational pull. The resulting shape will be an elliptical orbit. | If the comet’s speed is high, it will escape the sun’s gravitational pull. The resulting shape will be half a hyperbola. |
We see in this real life example, as in the definitions, a connection between ellipses and hyperbolas.
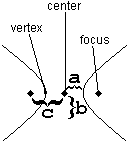
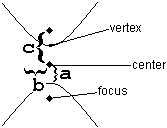
With hyperbolas, just as with ellipses, it is crucial to start by distinguishing horizontal from vertical. It is also useful to pay close attention to which aspects are the same as ellipses, and which are different.
| Horizontal | Vertical |
|---|---|
 |
 |
And of course, the usual rules of permutations apply. For instance, if we replace with , the hyperbola moves to the right by . So we have the more general form:
| Horizontal | Vertical |
|---|---|
The key to understanding hyperbolas is understanding the three constants , , and .
| Horizontal Hyperbola | Vertical Hyperbola | |
|---|---|---|
| Where are the foci? | Horizontally around the center | Vertically around the center |
| How far are the foci from the center? | ||
| What is the “transverse axis”? | The (horizontal) line from one vertex to the other | The (vertical) line from one vertex to the other |
| How long is the transverse axis? | ||
| Which is biggest? | is biggest. , and . | is biggest. , and . |
| crucial relationship |
Having trouble keeping it all straight? Let’s make a list of similarities and differences.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Advanced algebra ii: conceptual explanations' conversation and receive update notifications?