Mathematics
Common fractions
Educator section
Memorandum
18.1
ADDITION
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
PRODUCT
2
1
2
1
b) numerators x numerators
denominators x denominators
d)
(i)
= 2
(ii)
= 4
(iii)
= 9
18.2 3 1 2 8
- (i)
15 x
4 (ii)
18 x
40
8 5 25 27
2 1 5 3
k =
= 1
c =
= 1
7 4 3
18.3 b) (i) =
38 x
16 (ii) =
17 x
9
4 5 3 10
m = 28
n =
n =
6
(iii) =
18 x
8
5 3
1
=
p = 9
19.1
a) 1
b) 1
c) 1
d) 1
19.2
Product is 1 every time
19.4 a)
b)
c)
d)
19.5 c)
: First make an improper fraction (
)
d)
: First make an improper fraction (
)
20. a) 1
x
=
x
=
m = 83,
cm
b)
x
=
m
= 27,
cm
22.
(a) 32
(b) 15
(c) 25
(d) 25
(e) 45
(f) 2
(g) 8
(h) 7
(i) 7
(j) 6
(k) 6
(l) 8
(m) 8
(n) 8
(o) 100
Leaner section
Content
Activity: multiplication of fractions [lo 1.7.3, lo 2.1.5]
18. MULTIPLICATION OF FRACTIONS
18.1 Multiplication of fractions with natural numbers
You already know that multiplication is repeated addition.
a) See if you can complete the following table:
|
SUM |
SKETCH |
REPEATED ADDITION |
PRODUCT |
| e.g. |
5 ×
|
|
|
|
|
6 ×
|
|
.................................................. |
................. |
|
2 ×
|
|
.................................................. |
................. |
|
3 ×
|
|
.................................................. |
................. |
|
4 ×
|
|
.................................................. |
................. |
b) Look carefully at the completed table. Can you think of a shorter way/method to find the answers?
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
c) TAKE NOTE!
You could also follow this method:
1. Write both numbers as fractions e.g.
2. Multiply the numerators: 6 × 1 = 6
3. Multiply the denominators: 1 × 4 = 4
4. Simplify the answer:
d) Calculate:
(i)
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
(ii)
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
(iii)
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
e) We would represent
in another way using a number line:
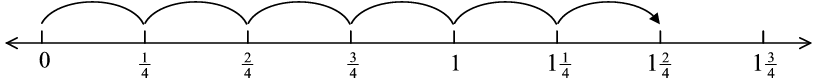
f) Represent the following on a number line:
18.2 Multiplying fractions with fractions
a) Look carefully at the following examples:
(i) Half (
) of three quarters (
) can be shown like this:

