| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Ray tracing is very useful for mirrors. The rules for ray tracing are summarized here for reference:
We use ray tracing to illustrate how images are formed by mirrors and to obtain numerical information about optical properties of the mirror. If we assume that a mirror is small compared with its radius of curvature, we can also use algebra and geometry to derive a mirror equation, which we do in the next section. Combining ray tracing with the mirror equation is a good way to analyze mirror systems.
For a plane mirror, we showed that the image formed has the same height and orientation as the object, and it is located at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror. Although the situation is a bit more complicated for curved mirrors, using geometry leads to simple formulas relating the object and image distances to the focal lengths of concave and convex mirrors.
Consider the object OP shown in [link] . The center of curvature of the mirror is labeled C and is a distance R from the vertex of the mirror, as marked in the figure. The object and image distances are labeled and , and the object and image heights are labeled and , respectively. Because the angles and are alternate interior angles, we know that they have the same magnitude. However, they must differ in sign if we measure angles from the optical axis, so . An analogous scenario holds for the angles and . The law of reflection tells us that they have the same magnitude, but their signs must differ if we measure angles from the optical axis. Thus, . Taking the tangent of the angles and , and using the property that , gives us
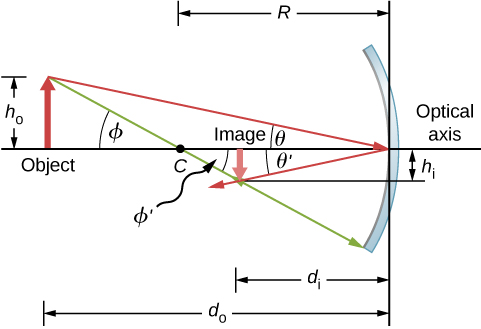
Similarly, taking the tangent of and gives
Combining these two results gives
After a little algebra, this becomes
No approximation is required for this result, so it is exact. However, as discussed above, in the small-angle approximation, the focal length of a spherical mirror is one-half the radius of curvature of the mirror, or . Inserting this into [link] gives the mirror equation :
The mirror equation relates the image and object distances to the focal distance and is valid only in the small-angle approximation. Although it was derived for a concave mirror, it also holds for convex mirrors (proving this is left as an exercise). We can extend the mirror equation to the case of a plane mirror by noting that a plane mirror has an infinite radius of curvature. This means the focal point is at infinity, so the mirror equation simplifies to

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?