| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
So far in this chapter, we have been discussing optical phenomena using the ray model of light. However, some phenomena require analysis and explanations based on the wave characteristics of light. This is particularly true when the wavelength is not negligible compared to the dimensions of an optical device, such as a slit in the case of diffraction . Huygens’s principle is an indispensable tool for this analysis.
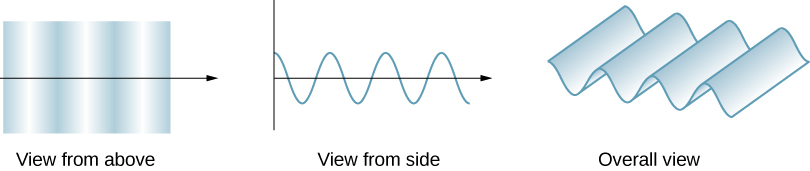
[link] shows how a transverse wave looks as viewed from above and from the side. A light wave can be imagined to propagate like this, although we do not actually see it wiggling through space. From above, we view the wave fronts (or wave crests) as if we were looking down on ocean waves. The side view would be a graph of the electric or magnetic field. The view from above is perhaps more useful in developing concepts about wave optics .
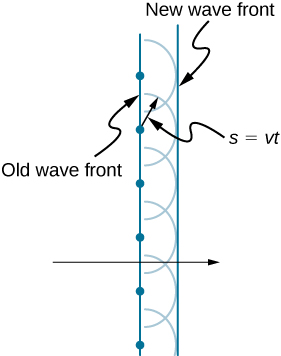
The Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens (1629–1695) developed a useful technique for determining in detail how and where waves propagate. Starting from some known position, Huygens’s principle states that every point on a wave front is a source of wavelets that spread out in the forward direction at the same speed as the wave itself. The new wave front is tangent to all of the wavelets.
[link] shows how Huygens’s principle is applied. A wave front is the long edge that moves, for example, with the crest or the trough. Each point on the wave front emits a semicircular wave that moves at the propagation speed v . We can draw these wavelets at a time t later, so that they have moved a distance The new wave front is a plane tangent to the wavelets and is where we would expect the wave to be a time t later. Huygens’s principle works for all types of waves, including water waves, sound waves, and light waves. It is useful not only in describing how light waves propagate but also in explaining the laws of reflection and refraction. In addition, we will see that Huygens’s principle tells us how and where light rays interfere.
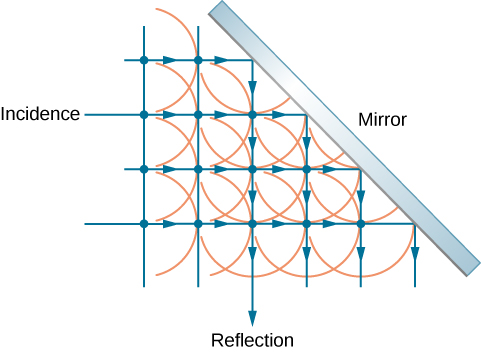
[link] shows how a mirror reflects an incoming wave at an angle equal to the incident angle, verifying the law of reflection. As the wave front strikes the mirror, wavelets are first emitted from the left part of the mirror and then from the right. The wavelets closer to the left have had time to travel farther, producing a wave front traveling in the direction shown.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?