| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
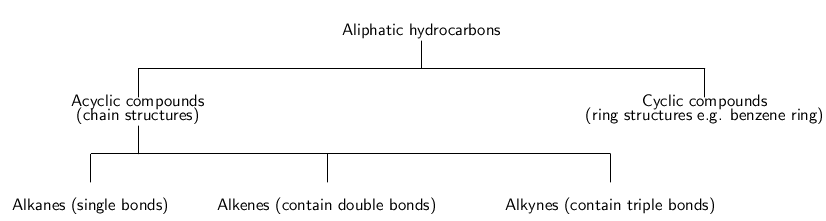
Let us first look at a group of organic compounds known as the hydrocarbons . These molecules only contain carbon and hydrogen. The hydrocarbons that we are going to look at are called aliphatic compounds . The aliphatic compounds are divided into acyclic compounds (chain structures) and cyclic compounds (ring structures). The chain structures are further divided into structures that contain only single bonds ( alkanes ), those that contain at least one double bond ( alkenes ) and those that contain at least one triple bond ( alkynes ). Cyclic compounds include structures such as the benzene ring . [link] summarises the classification of the hydrocarbons.
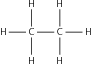
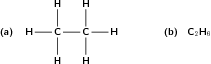
Hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds are called saturated hydrocarbons because each carbon atom is bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as possible. [link] shows a molecule of ethane which is a saturated hydrocarbon.
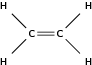
Hydrocarbons that contain double or triple bonds are called unsaturated hydrocarbons because they don't contain as many hydrogen atoms as possible. [link] shows a molecule of ethene which is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. If you compare the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in a molecule of ethane and a molecule of ethene, you will see that the number of hydrogen atoms in ethene is less than the number of hydrogen atoms in ethane despite the fact that they both contain two carbon atoms. In order for an unsaturated compound to become saturated, a double bond has to be broken, and another two hydrogen atoms added for each double bond that is replaced by a single bond.
Fat that occurs naturally in living matter such as animals and plants is used as food for human consumption and contains varying proportions of saturated and unsaturated fat. Foods that contain a high proportion of saturated fat are butter, ghee, suet, tallow, lard, coconut oil, cottonseed oil, and palm kernel oil, dairy products (especially cream and cheese), meat, and some prepared foods. Diets high in saturated fat are correlated with an increased incidence of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease according to a number of studies. Vegetable oils contain unsaturated fats and can be hardened to form margarine by adding hydrogen on to some of the carbon=carbon double bonds using a nickel catalyst. The process is called hydrogenation
We will now go on to look at each of the hydrocarbon groups in more detail. These groups are the alkanes, the alkenes and the alkynes.
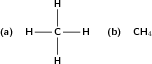
The alkanes are hydrocarbons that only contain single covalent bonds between their carbon atoms. This means that they are saturated compounds and are quite unreactive. The simplest alkane has only one carbon atom and is called methane . This molecule is shown in [link] .
The second alkane in the series has two carbon atoms and is called ethane . This is shown in [link] .
The third alkane in the series has three carbon atoms and is called propane ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?