| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
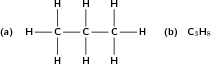
When you look at the molecular formula for each of the alkanes, you should notice a pattern developing. For each carbon atom that is added to the molecule, two hydrogen atoms are added. In other words, each molecule differs from the one before it by CH . This is called a homologous series . The alkanes have the general formula C H .
The alkanes are the most important source of fuel in the world and are used extensively in the chemical industry. Some are gases (e.g. methane and ethane), while others are liquid fuels (e.g. octane, an important component of petrol).
Some fungi use alkanes as a source of carbon and energy. One fungus Amorphotheca resinae prefers the alkanes used in aviation fuel, and this can cause problems for aircraft in tropical areas!
In order to give compounds a name, certain rules must be followed. When naming organic compounds, the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature is used. We will first look at some of the steps that need to be followed when naming a compound, and then try to apply these rules to some specific examples.
| Carbon atoms | prefix |
| 1 | meth(ane) |
| 2 | eth(ane) |
| 3 | prop(ane) |
| 4 | but(ane) |
| 5 | pent(ane) |
| 6 | hex(ane) |
| 7 | hept(ane) |
| 8 | oct(ane) |
| 9 | non(ane) |
| 10 | dec(ane) |
Khan academy video on alkanes
Give the IUPAC name for the following compound:
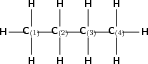
Note: The numbers attached to the carbon atoms would not normally be shown. The atoms have been numbered to help you to name the compound.
The compound is a hydrocarbon with single bonds between the carbon atoms. It is an alkane and will have a suffix of -ane.
There are four carbon atoms in the longest chain. The prefix of the compound will be 'but'.
In this case, it is easy. The carbons are numbered from left to right, from one to four.
There are no branched groups in this compound.
The name of the compound is butane .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?