| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A man walks 40 m East, then 30 m North.
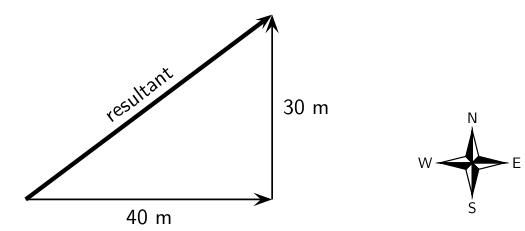
In the first part of his journey he traveled 40 m and in the second part he traveled 30 m. This gives us a total distance traveled of 40 m + 30 m = 70 m.
The man's resultant displacement is the vector from where he started to where he ended. It is the vector sum of his two separate displacements. We will use the head-to-tail method of accurate construction to find this vector.
A scale of 1 cm represents 10 m (1 cm = 10 m) is a good choice here. Now we can begin the process of construction.
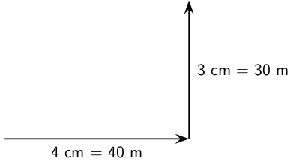
We draw the first displacement as an arrow 4 cm long in an eastwards direction.
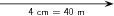
Starting from the head of the first vector we draw the second vector as an arrow 3 cm long in a northerly direction.
Now we connect the starting point to the end point and measure the length and direction of this arrow (the resultant).
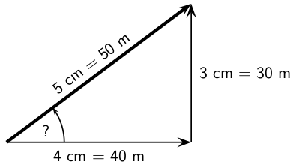
To find the direction you measure the angle between the resultant and the 40 m vector. You should get about 37 .
Finally we use the scale to convert the length of the resultant in the scale diagram to the actual magnitude of the resultantdisplacement. According to the chosen scale 1 cm = 10 m. Therefore 5 cm represents 50 m. The resultant displacement is then 50 m 37 north of east.
Phet simulation for vectors
The parallelogram method is another graphical technique of finding the resultant of two vectors.
Method: The Parallelogram Method
A force of is applied to a block in a horizontal direction. A second force is applied to the object at an angle of 30 above the horizontal.
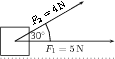
Determine the resultant force acting on the block using the parallelogram method of accurate construction.

In this problem a scale of 1 cm = 1 N would be appropriate, since then the vector diagram would take up a reasonable fraction of the page. We can now begin the accurate scale diagram.
Let us draw first. According to the scale it has length 5 cm.

Next we draw . According to the scale it has length 4 cm. We make use of a protractor to draw this vector at 30 to the horizontal.
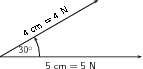
Next we complete the parallelogram and draw the diagonal.
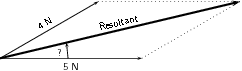
The resultant has a measured length of 8,7 cm.
We use a protractor to measure the angle between the horizontal and the resultant. We get 13,3 .
Finally we use the scale to convert the measured length into the actual magnitude. Since 1 cm = 1 N, 8,7 cm represents 8,7 N. Therefore the resultant force is 8,7 N at 13,3 above the horizontal.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?