| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Questions and their answers are presented here in the module text format as if it were an extension of the treatment of the topic. The idea is to provide a verbose explanation, detailing the application of theory. Solution presented is, therefore, treated as the part of the understanding process – not merely a Q/A session. The emphasis is to enforce ideas and concepts, which can not be completely absorbed unless they are put to real time situation.
We discuss problems, which highlight certain aspects of the study leading to the balanced force system. The questions are categorized in terms of the characterizing features of the subject matter :
Problem 1 : A block weighing 100 N is suspended with the help of three strings as shown in the figure. Find the tension in each of the strings.
Balanced force system
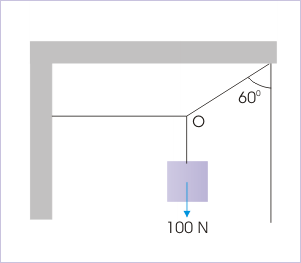
Solution : This example illustrates one important aspect of force diagram. We can even draw force diagram of a point on the system like “O”, where three strings meet. The point does not represent a body, but force diagram is valid so long we display the forces acting through the point, O.
Let , and be the tensions in the string as shown in the figure here.
Balanced force system
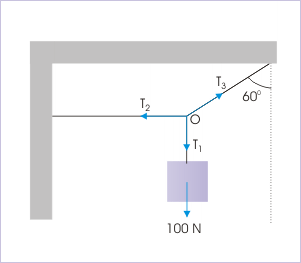
A preliminary assessment of forces suggests that analysis of forces on block will provide value for the unknown, . Hence, we first analyze force on the block.
Free body diagram
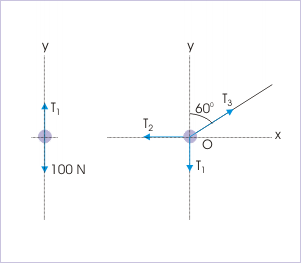
The external forces at point “O” are (i) Tension, (ii) Tension, and (iii) Tension,
and
Putting this in the equation for , we have :
We should note that direction of tension " " acts up with respect to the body, whereas " " acts down with respect to point "O". We need not be overly concerned and just try to figure out, what a taut string does to the body or point in consideration. The tension pulls down the point "O" and pulls up the body. For this reason, it has different directions with respect to them.
Problem 3 : Find the force, F, required to keep the block stationary on an incline of angle "θ" having friction-less surface as shown in the figure.
Balanced force system
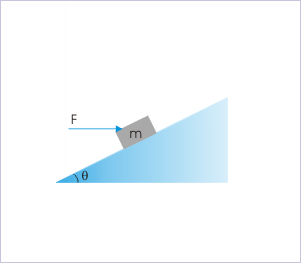
Solution : We can either have (a) axes in horizontal and vertical directions or (b) parallel to incline and perpendicular to it. Which of the two is better suited here ? In this case, one force (mg) is along vertical direction, whereas other external force (F) is along horizontal direction. As such, it is advantageous to have a horizontal and vertical axes as two of three forces are along the coordinate axes.
The external forces on the block are (i) Force, F (ii) Weight, mg and (iii) Normal force, N.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?