| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Is it a tumor? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can tell. Your head is full of tiny radio transmitters (the nuclear spins of the hydrogen nuclei of your water molecules). In an MRI unit, these little radios can be made to broadcast their positions, giving a detailed picture of the inside of your head.

In terms of radiation dose, what is the major difference between medical diagnostic uses of radiation and medical therapeutic uses?
One of the methods used to limit radiation dose to the patient in medical imaging is to employ isotopes with short half-lives. How would this limit the dose?
A neutron generator uses an source, such as radium, to bombard beryllium, inducing the reaction . Such neutron sources are called RaBe sources, or PuBe sources if they use plutonium to get the s. Calculate the energy output of the reaction in MeV.
5.701 MeV
Neutrons from a source (perhaps the one discussed in the preceding problem) bombard natural molybdenum, which is 24 percent . What is the energy output of the reaction ? The mass of is given in Appendix A: Atomic Masses , and that of is 98.907711 u.
The purpose of producing (usually by neutron activation of natural molybdenum, as in the preceding problem) is to produce Using the rules, verify that the decay of produces . (Most nuclei produced in this decay are left in a metastable excited state denoted .)
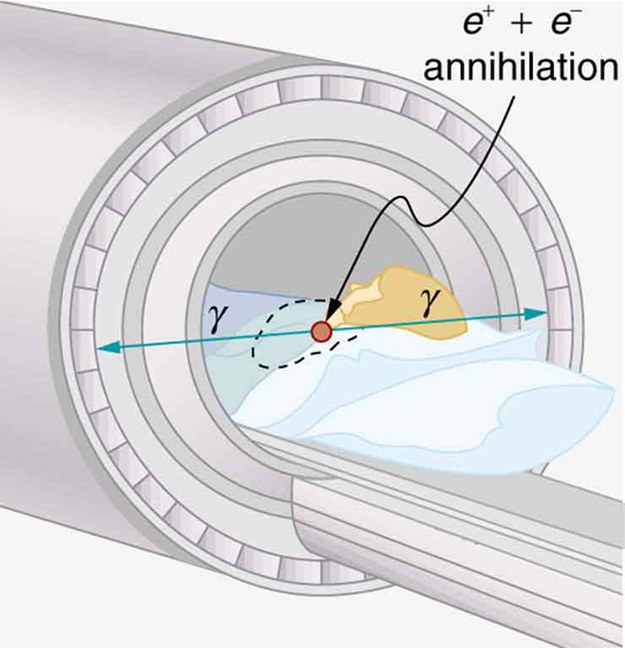
(a) Two annihilation rays in a PET scan originate at the same point and travel to detectors on either side of the patient. If the point of origin is 9.00 cm closer to one of the detectors, what is the difference in arrival times of the photons? (This could be used to give position information, but the time difference is small enough to make it difficult.)
(b) How accurately would you need to be able to measure arrival time differences to get a position resolution of 1.00 mm?
[link] indicates that 7.50 mCi of is used in a brain scan. What is the mass of technetium?
The activities of and used in thyroid scans are given in [link] to be 50 and , respectively. Find and compare the masses of and in such scans, given their respective half-lives are 8.04 d and 13.2 h. The masses are so small that the radioiodine is usually mixed with stable iodine as a carrier to ensure normal chemistry and distribution in the body.
(a) Neutron activation of sodium, which is 100% , produces , which is used in some heart scans, as seen in [link] . The equation for the reaction is . Find its energy output, given the mass of is 23.990962 u.
(b) What mass of produces the needed 5.0-mCi activity, given its half-life is 15.0 h?
(a) 6.958 MeV
(b)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Basic physics for medical imaging' conversation and receive update notifications?