| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The preservation of medical laboratory blood samples, mining of sea water for magnesium, formulation of over-the-counter medicines such as Milk of Magnesia and antacids, and treating the presence of hard water in your home’s water supply are just a few of the many tasks that involve controlling the equilibrium between a slightly soluble ionic solid and an aqueous solution of its ions.
In some cases, we want to prevent dissolution from occurring. Tooth decay, for example, occurs when the calcium hydroxylapatite, which has the formula Ca 5 (PO 4 ) 3 (OH), in our teeth dissolves. The dissolution process is aided when bacteria in our mouths feast on the sugars in our diets to produce lactic acid, which reacts with the hydroxide ions in the calcium hydroxylapatite. Preventing the dissolution prevents the decay. On the other hand, sometimes we want a substance to dissolve. We want the calcium carbonate in a chewable antacid to dissolve because the ions produced in this process help soothe an upset stomach.
In this section, we will find out how we can control the dissolution of a slightly soluble ionic solid by the application of Le Châtelier’s principle. We will also learn how to use the equilibrium constant of the reaction to determine the concentration of ions present in a solution.
Silver chloride is what’s known as a sparingly soluble ionic solid ( [link] ). Recall from the solubility rules in an earlier chapter that halides of Ag + are not normally soluble. However, when we add an excess of solid AgCl to water, it dissolves to a small extent and produces a mixture consisting of a very dilute solution of Ag + and Cl – ions in equilibrium with undissolved silver chloride:
This equilibrium, like other equilibria, is dynamic; some of the solid AgCl continues to dissolve, but at the same time, Ag + and Cl – ions in the solution combine to produce an equal amount of the solid. At equilibrium, the opposing processes have equal rates.
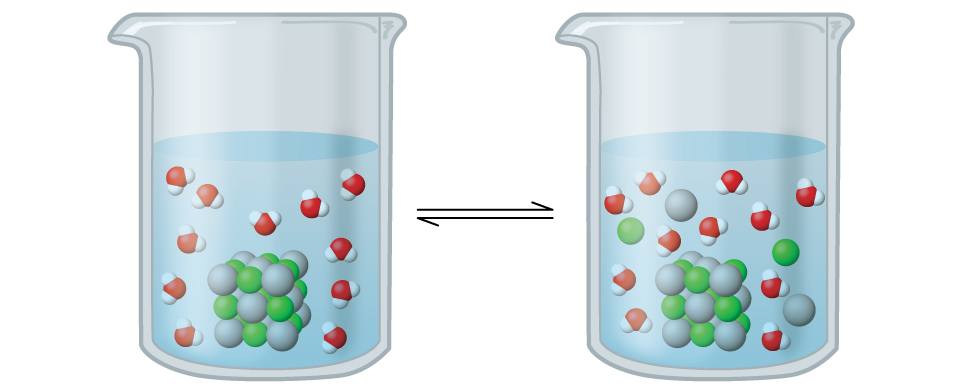
The equilibrium constant for the equilibrium between a slightly soluble ionic solid and a solution of its ions is called the solubility product ( K sp ) of the solid. Recall from the chapter on solutions and colloids that we use an ion’s concentration as an approximation of its activity in a dilute solution. For silver chloride, at equilibrium:
When looking at dissolution reactions such as this, the solid is listed as a reactant, whereas the ions are listed as products. The solubility product constant, as with every equilibrium constant expression, is written as the product of the concentrations of each of the ions, raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients. Here, the solubility product constant is equal to Ag + and Cl – when a solution of silver chloride is in equilibrium with undissolved AgCl. There is no denominator representing the reactants in this equilibrium expression since the reactant is a pure solid; therefore [AgCl] does not appear in the expression for K sp .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?