| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When a fluid flows into a narrower channel, its speed increases. That means its kinetic energy also increases. Where does that change in kinetic energy come from? The increased kinetic energy comes from the net work done on the fluid to push it into the channel and the work done on the fluid by the gravitational force, if the fluid changes vertical position. Recall the work-energy theorem,
There is a pressure difference when the channel narrows. This pressure difference results in a net force on the fluid: recall that pressure times area equals force. The net work done increases the fluid’s kinetic energy. As a result, the pressure will drop in a rapidly-moving fluid , whether or not the fluid is confined to a tube.
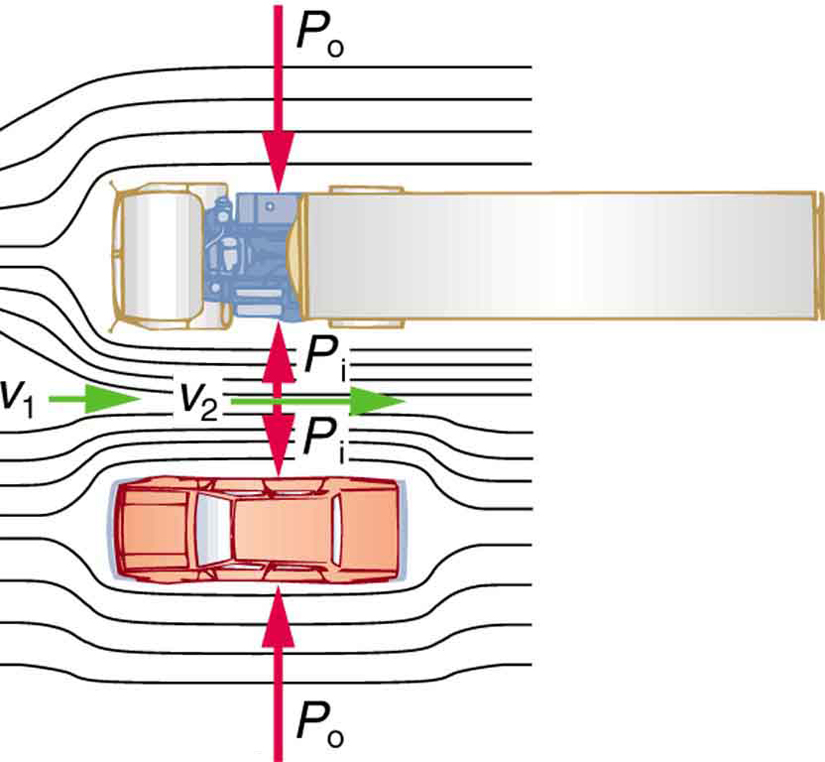
There are a number of common examples of pressure dropping in rapidly-moving fluids. Shower curtains have a disagreeable habit of bulging into the shower stall when the shower is on. The high-velocity stream of water and air creates a region of lower pressure inside the shower, and standard atmospheric pressure on the other side. The pressure difference results in a net force inward pushing the curtain in. You may also have noticed that when passing a truck on the highway, your car tends to veer toward it. The reason is the same—the high velocity of the air between the car and the truck creates a region of lower pressure, and the vehicles are pushed together by greater pressure on the outside. (See [link] .) This effect was observed as far back as the mid-1800s, when it was found that trains passing in opposite directions tipped precariously toward one another.
Hold the short edge of a sheet of paper parallel to your mouth with one hand on each side of your mouth. The page should slant downward over your hands. Blow over the top of the page. Describe what happens and explain the reason for this behavior.
The relationship between pressure and velocity in fluids is described quantitatively by Bernoulli’s equation , named after its discoverer, the Swiss scientist Daniel Bernoulli (1700–1782). Bernoulli’s equation states that for an incompressible, frictionless fluid, the following sum is constant:
where is the absolute pressure, is the fluid density, is the velocity of the fluid, is the height above some reference point, and is the acceleration due to gravity. If we follow a small volume of fluid along its path, various quantities in the sum may change, but the total remains constant. Let the subscripts 1 and 2 refer to any two points along the path that the bit of fluid follows; Bernoulli’s equation becomes

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics ii' conversation and receive update notifications?