| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The order Lactobacillales comprises low G+C gram-positive bacteria that include both bacilli and cocci in the genera Lactobacillus , Leuconostoc , Enterococcus , and Streptococcus . Bacteria of the latter three genera typically are spherical or ovoid and often form chains.
Streptococcus , the name of which comes from the Greek word for twisted chain , is responsible for many types of infectious diseases in humans. Species from this genus, often referred to as streptococci , are usually classified by serotypes called Lancefield groups, and by their ability to lyse red blood cells when grown on blood agar.
S. pyogenes belongs to the Lancefield group A, β-hemolytic Streptococcus . This species is considered a pyogenic pathogen because of the associated pus production observed with infections it causes ( [link] ). S. pyogenes is the most common cause of bacterial pharyngitis ( strep throat ); it is also an important cause of various skin infections that can be relatively mild (e.g., impetigo ) or life threatening (e.g., necrotizing fasciitis , also known as flesh eating disease), life threatening.
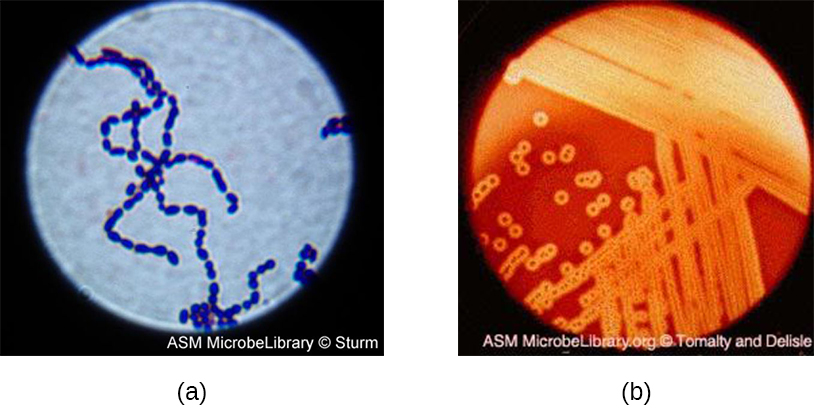
The nonpyogenic (i.e., not associated with pus production) streptococci are a group of streptococcal species that are not a taxon but are grouped together because they inhabit the human mouth. The nonpyogenic streptococci do not belong to any of the Lancefield groups. Most are commensals, but a few, such as S. mutans , are implicated in the development of dental caries.
S. pneumoniae (commonly referred to as pneumococcus), is a Streptococcus species that also does not belong to any Lancefield group . S. pneumoniae cells appear microscopically as diplococci, pairs of cells, rather than the long chains typical of most streptococci. Scientists have known since the 19th century that S. pneumoniae causes pneumonia and other respiratory infections. However, this bacterium can also cause a wide range of other diseases, including meningitis, septicemia, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis, especially in newborns, the elderly, and patients with immunodeficiency.
The name of the class Bacilli suggests that it is made up of bacteria that are bacillus in shape, but it is a morphologically diverse class that includes bacillus-shaped and cocccus-shaped genera. Among the many genera in this class are two that are very important clinically: Bacillus and Staphylococcus .
Bacteria in the genus Bacillus are bacillus in shape and can produce endospores . They include aerobes or facultative anaerobes. A number of Bacillus spp. are used in various industries, including the production of antibiotics (e.g., barnase), enzymes (e.g., alpha-amylase, BamH1 restriction endonuclease), and detergents (e.g., subtilisin).
Two notable pathogens belong to the genus Bacillus. B. anthracis is the pathogen that causes anthrax , a severe disease that affects wild and domesticated animals and can spread from infected animals to humans. Anthrax manifests in humans as charcoal-black ulcers on the skin, severe enterocolitis, pneumonia, and brain damage due to swelling. If untreated, anthrax is lethal. B. cereus , a closely related species, is a pathogen that may cause food poisoning. It is a rod-shaped species that forms chains. Colonies appear milky white with irregular shapes when cultured on blood agar ( [link] ). One other important species is B. thuringiensis . This bacterium produces a number of substances used as insecticides because they are toxic for insects.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?