| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
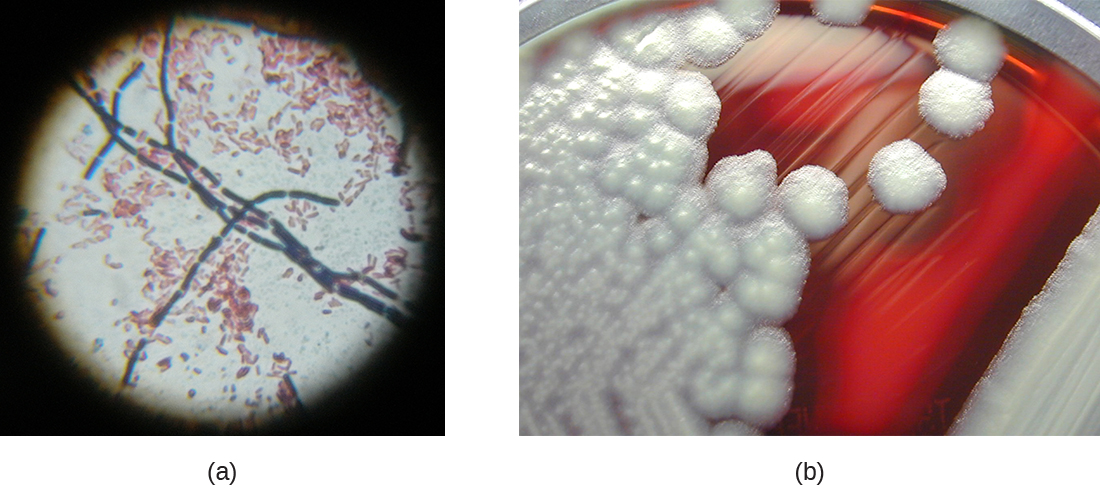
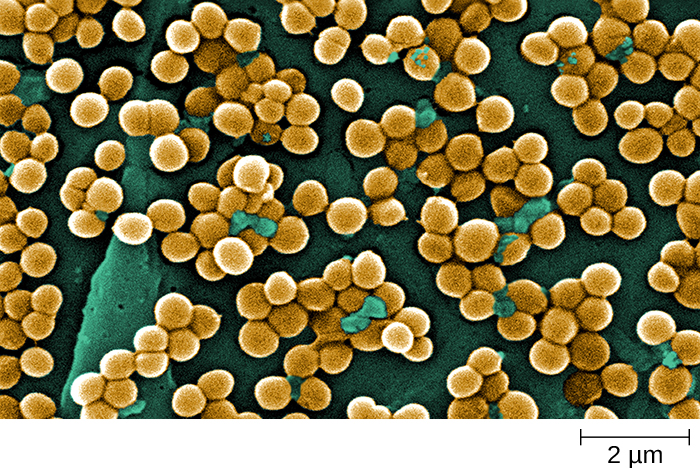
The genus Staphylococcus also belongs to the class Bacilli, even though its shape is coccus rather than a bacillus. The name Staphylococcus comes from a Greek word for bunches of grapes , which describes their microscopic appearance in culture ( [link] ). Staphylococcus spp. are facultative anaerobic, halophilic, and nonmotile. The two best-studied species of this genus are S. epidermidis and S. aureus .
S. epidermidis , whose main habitat is the human skin, is thought to be nonpathogenic for humans with healthy immune systems, but in patients with immunodeficiency, it may cause infections in skin wounds and prostheses (e.g., artificial joints, heart valves) . S. epidermidis is also an important cause of infections associated with intravenous catheters. This makes it a dangerous pathogen in hospital settings, where many patients may be immunocompromised.
Strains of S. aureus cause a wide variety of infections in humans, including skin infections that produce boils, carbuncles, cellulitis, or impetigo. Certain strains of S. aureus produce a substance called enterotoxin , which can cause severe enteritis, often called staph food poisoning. Some strains of S. aureus produce the toxin responsible for toxic shock syndrome , which can result in cardiovascular collapse and death.
Many strains of S. aureus have developed resistance to antibiotics. Some antibiotic-resistant strains are designated as methicillin-resistant S. aureus ( MRSA ) and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA) . These strains are some of the most difficult to treat because they exhibit resistance to nearly all available antibiotics, not just methicillin and vancomycin. Because they are difficult to treat with antibiotics, infections can be lethal. MRSA and VRSA are also contagious, posing a serious threat in hospitals, nursing homes, dialysis facilities, and other places where there are large populations of elderly, bedridden, and/or immunocompromised patients. Appendix D lists the genera, species, and related diseases for bacilli.
Although Mycoplasma spp. do not possess a cell wall and, therefore, are not stained by Gram-stain reagents, this genus is still included with the low G+C gram-positive bacteria. The genus Mycoplasma includes more than 100 species, which share several unique characteristics. They are very small cells, some with a diameter of about 0.2 μm, which is smaller than some large viruses. They have no cell walls and, therefore, are pleomorphic , meaning that they may take on a variety of shapes and can even resemble very small animal cells. Because they lack a characteristic shape, they can be difficult to identify. One species, M. pneumoniae , causes the mild form of pneumonia known as “ walking pneumonia ” or “ atypical pneumonia .” This form of pneumonia is typically less severe than forms caused by other bacteria or viruses.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?