| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The low G+C gram-positive bacteria have less than 50% guanine and cytosine in their DNA, and this group of bacteria includes a number of genera of bacteria that are pathogenic.
Based on her symptoms, Marsha’s doctor suspected that she had a case of tuberculosis. Although less common in the United States, tuberculosis is still extremely common in many parts of the world, including Nigeria. Marsha’s work there in a medical lab likely exposed her to Mycobacterium tuberculosis , the bacterium that causes tuberculosis.
Marsha’s doctor ordered her to stay at home, wear a respiratory mask, and confine herself to one room as much as possible. He also said that Marsha had to take one semester off school. He prescribed isoniazid and rifampin, antibiotics used in a drug cocktail to treat tuberculosis, which Marsha was to take three times a day for at least three months.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
One large and diverse class of low G+C gram-positive bacteria is Clostridia. The best studied genus of this class is Clostridium . These rod-shaped bacteria are generally obligate anaerobes that produce endospores and can be found in anaerobic habitats like soil and aquatic sediments rich in organic nutrients. The endospores may survive for many years.
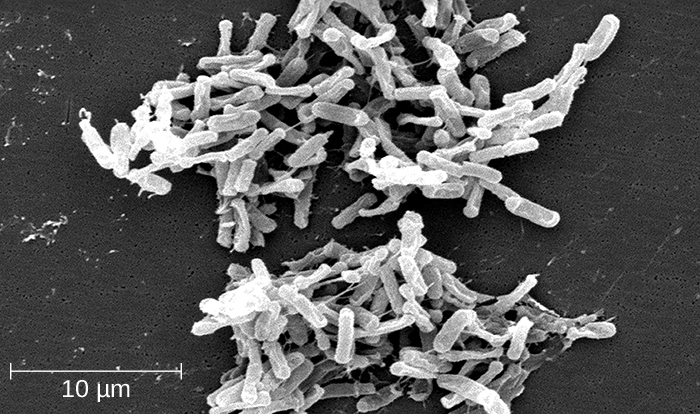
Clostridium spp. produce more kinds of protein toxins than any other bacterial genus, and several species are human pathogens. C. perfringens is the third most common cause of food poisoning in the United States and is the causative agent of an even more serious disease called gas gangrene . Gas gangrene occurs when C. perfringens endospores enter a wound and germinate, becoming viable bacterial cells and producing a toxin that can cause the necrosis (death) of tissue. C. tetani , which causes tetanus , produces a neurotoxin that is able to enter neurons, travel to regions of the central nervous system where it blocks the inhibition of nerve impulses involved in muscle contractions, and cause a life-threatening spastic paralysis. C. botulinum produces botulinum neurotoxin , the most lethal biological toxin known. Botulinum toxin is responsible for rare but frequently fatal cases of botulism . The toxin blocks the release of acetylcholine in neuromuscular junctions, causing flaccid paralysis. In very small concentrations, botulinum toxin has been used to treat muscle pathologies in humans and in a cosmetic procedure to eliminate wrinkles. C. difficile is a common source of hospital-acquired infections ( [link] ) that can result in serious and even fatal cases of colitis (inflammation of the large intestine). Infections often occur in patients who are immunosuppressed or undergoing antibiotic therapy that alters the normal microbiota of the gastrointestinal tract. Appendix D lists the genera, species, and related diseases for Clostridia.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?