| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
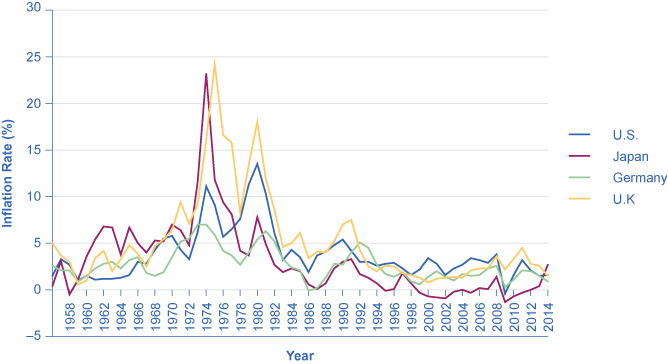
Around the rest of the world, the pattern of inflation has been very mixed, as can be seen in [link] which shows inflation rates over the last several decades. Many industrialized countries, not just the United States, had relatively high inflation rates in the 1970s. For example, in 1975, Japan’s inflation rate was over 8% and the inflation rate for the United Kingdom was almost 25%. In the 1980s, inflation rates came down in the United States and in Europe and have largely stayed down.
Countries with controlled economies in the 1970s, like the Soviet Union and China, historically had very low rates of measured inflation—because prices were forbidden to rise by law, except for the cases where the government deemed a price increase to be due to quality improvements. However, these countries also had perpetual shortages of goods, since forbidding prices to rise acts like a price ceiling and creates a situation where quantity demanded often exceeds quantity supplied. As Russia and China made a transition toward more market-oriented economies, they also experienced outbursts of inflation, although the statistics for these economies should be regarded as somewhat shakier. Inflation in China averaged about 10% per year for much of the 1980s and early 1990s, although it has dropped off since then. Russia experienced hyperinflation —an outburst of high inflation—of 2,500% per year in the early 1990s, although by 2006 Russia’s consumer price inflation had dipped below 10% per year, as shown in [link] . The closest the United States has ever gotten to hyperinflation was during the Civil War, 1860–1865, in the Confederate states.
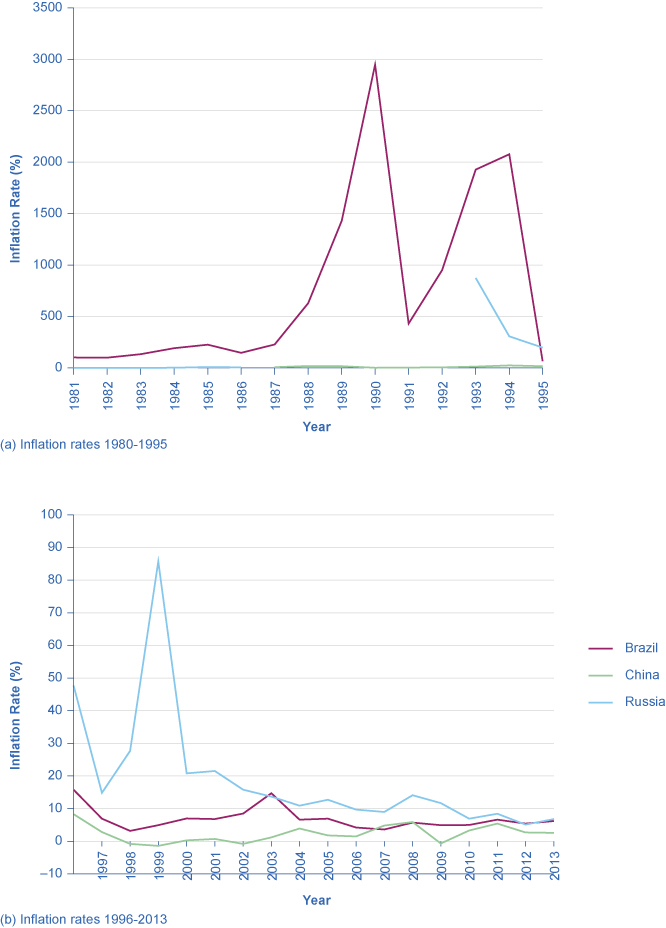
Many countries in Latin America experienced raging hyperinflation during the 1980s and early 1990s, with inflation rates often well above 100% per year. In 1990, for example, both Brazil and Argentina saw inflation climb above 2000%. Certain countries in Africa experienced extremely high rates of inflation, sometimes bordering on hyperinflation, in the 1990s. Nigeria, the most populous country in Africa, had an inflation rate of 75% in 1995.
In the early 2000s, the problem of inflation appears to have diminished for most countries, at least in comparison to the worst times of recent decades. As we noted in this earlier Bring it Home feature, in recent years, the world’s worst example of hyperinflation was in Zimbabwe, where at one point the government was issuing bills with a face value of $100 trillion (in Zimbabwean dollars)—that is, the bills had $100,000,000,000,000 written on the front, but were almost worthless. In many countries, the memory of double-digit, triple-digit, and even quadruple-digit inflation is not very far in the past.
In the U.S. economy, the annual inflation rate in the last two decades has typically been around 2% to 4%. The periods of highest inflation in the United States in the twentieth century occurred during the years after World Wars I and II, and in the 1970s. The period of lowest inflation—actually, with deflation—was the Great Depression of the 1930s.
Within 1 or 2 percentage points, what has the U.S. inflation rate been during the last 20 years? Draw a graph to show the data.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?