| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
In the last three decades, inflation has been relatively low in the U.S. economy, with the Consumer Price Index typically rising 2% to 4% per year. Looking back over the twentieth century, there have been several periods where inflation caused the price level to rise at double-digit rates, but nothing has come close to hyperinflation.
[link] (a) shows the level of prices in the Consumer Price Index stretching back to 1916. In this case, the base years (when the CPI is defined as 100) are set for the average level of prices that existed from 1982 to 1984. [link] (b) shows the annual percentage changes in the CPI over time, which is the inflation rate.
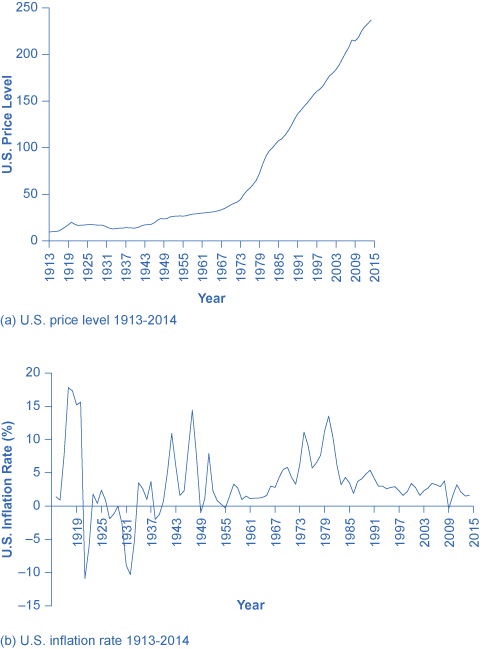
The first two waves of inflation are easy to characterize in historical terms: they are right after World War I and World War II. However, there are also two periods of severe negative inflation—called deflation —in the early decades of the twentieth century: one following the deep recession of 1920–21 and the other during the Great Depression of the 1930s. (Since inflation is a time when the buying power of money in terms of goods and services is reduced, deflation will be a time when the buying power of money in terms of goods and services increases.) For the period from 1900 to about 1960, the major inflations and deflations nearly balanced each other out, so the average annual rate of inflation over these years was only about 1% per year. A third wave of more severe inflation arrived in the 1970s and departed in the early 1980s.
Visit this website to use an inflation calculator and discover how prices have changed in the last 100 years.
Times of recession or depression often seem to be times when the inflation rate is lower, as in the recession of 1920–1921, the Great Depression, the recession of 1980–1982, and the Great Recession in 2008–2009. There were a few months in 2009 that were deflationary, but not at an annual rate. Recessions are typically accompanied by higher levels of unemployment, and the total demand for goods falls, pulling the price level down. Conversely, the rate of inflation often, but not always, seems to start moving up when the economy is growing very strongly, like right after wartime or during the 1960s. The frameworks for macroeconomic analysis, developed in other chapters, will explain why recession often accompanies higher unemployment and lower inflation, while rapid economic growth often brings lower unemployment but higher inflation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?