| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
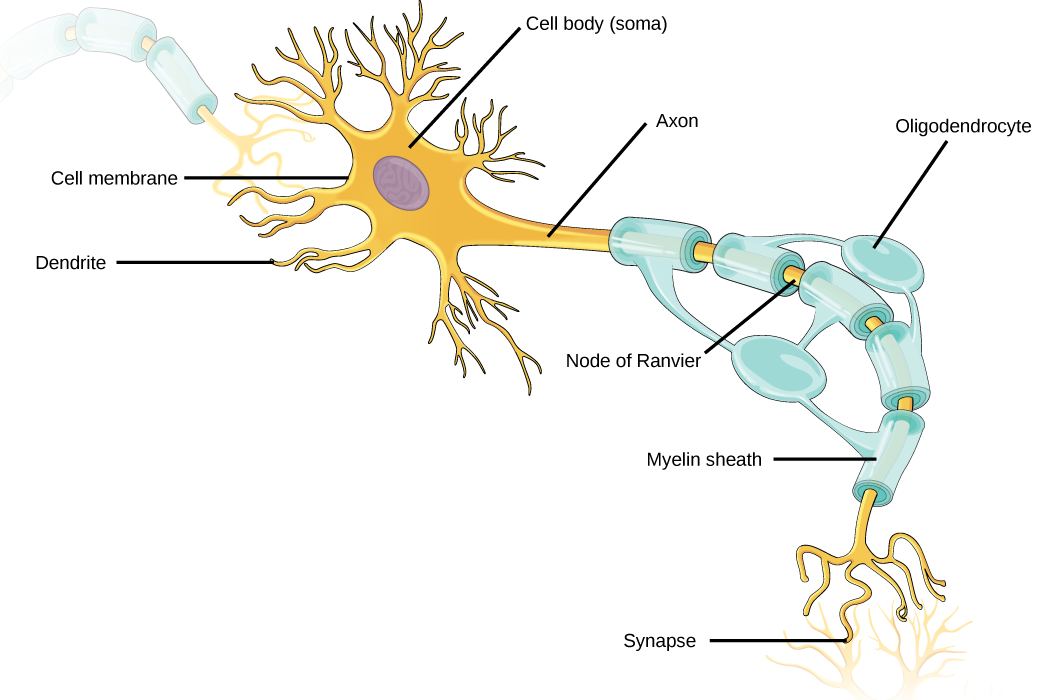
Once a signal is received by the dendrite, it then travels to the cell body. The cell body contains a specialized structure, the axon hillock, that integrates signals from multiple synapses and serves as a junction between the cell body and an axon . An axon is a tube-like structure that propagates the integrated signal to specialized endings called axon terminals. These terminals in turn synapse on other neurons, muscle, or target organs. Chemicals (known as neurotransmitters) released at axon terminals allow signals to be communicated to these other cells. Neurons usually have one or two axons, but some neurons, like amacrine cells in the retina, do not contain any axons. Some axons are covered with myelin (a product of the glial cells), which acts as an insulator and greatly increases the speed of conduction. Along the axon there are periodic gaps in the myelin sheath. These gaps are called nodes of Ranvier and are sites where the signal is “recharged” as it travels along the axon.
It is important to note that a single neuron does not act alone—neuronal communication depends on the connections that neurons make with one another (as well as with other cells, like muscle cells). Dendrites from a single neuron may receive synaptic contact from many other neurons. For example, dendrites from a Purkinje cell in the cerebellum are thought to receive contact from as many as 200,000 other neurons.
There are different types of neurons, and the functional role of a given neuron is intimately dependent on its structure. Although there are only three functional types of neurons [link] , an amazing diversity of neuron shapes and sizes can found in different parts of the nervous system (and across species).
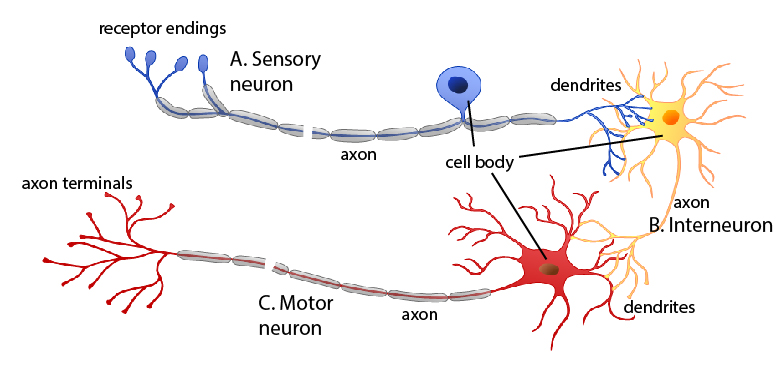
While there are many defined neuron cell shapes, neurons are broadly divided into three basic types: sensory, interneuron, and motor neuron. In general, sensory neurons detect information, either from the external environment or from internal sources. Examples of sensory neurons include the pain receptors in your skin and the photoreceptors in your retina. When activated by the signal to which they are attuned, they send information (via an action potential) to an interneuron. Interneurons both receive signals from other neurons and transmit signals to other neurons. The majority of the cells in your brain and spinal cord are interneurons, communicating only with other neurons. Interneurons can also send a signal to motor neurons , which control muscles and endocrine glands.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?