| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Some animals can detect magnetic fields, whichhelps them orientate themselves and navigate. Animals which can do this include pigeons, bees, Monarch butterflies, sea turtles and certain fish.
In the picture below, you can see a representation of the earth's magnetic field which is very similar to the magnetic field of a giant bar magnet likethe one on the right of the picture. So the earth has two sets of north poles and south poles: geographic poles and magnetic poles .
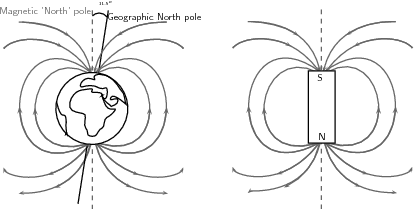
The earth's magnetic field is thought to be caused by flowing liquid metals in the outer core which causes electric currents and a magnetic field. From the pictureyou can see that the direction of magnetic north and true north are not identical. The geographic north pole , which is the point through which the earth's rotation axis goes, is about 11,5 o away from the direction of the magnetic north pole (which is where a compass will point). However, the magnetic poles shift slightly all the time.
Another interesting thing to note is that if we think of the earth as a big bar magnet, and we know that magnetic field lines always point from north to south , then the compass tells us that what we call the magnetic north pole is actually the south pole of the bar magnet!
The direction of the earth's magnetic field flips direction about once every 200 000 years! You can picture this as a bar magnet whose north and south poleperiodically switch sides. The reason for this is still not fully understood.
The earth's magnetic field is very important for humans and other animals on earth because it protects us from being bombarded (hit) by high energy charged particles which are emitted by the Sun. The stream of charged particles (mainly positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons) coming from the sun is called the solar wind. When these particles come close to the Earth, they become trapped by the Earth's magnetic field and cannot shower down to the surface where they can harm living organisms. Astronauts in space are at risk of being irradiated by the solar wind because they are outside the zones where the charged particles are trapped.
The region above Earth's atmosphere in which charged particles are affected by Earth's magnetic field is called the magnetosphere. Relatively often, in addition to the usual solar wind, the Sun may eject a large bubble of material (protons and electrons) with its own magnetic field from its outer atmosphere. Sometimes these bubbles travel towards the Earth where their magnetic fields can join with Earth's magnetic field. When this happens a huge amount of energy is released into the Earth's magnetosphere, causing a geomagnetic storm. These storms cause rapid changes in the Earth's magnetosphere which in turn may affect electric and magnetic systems on the Earth such as power grids, cellphone networks, and other electronic systems.
Another effect caused by the Earth's magnetic field is the spectacular Northern and Southern Lights, which are also called the Aurora Borealis and the Aurora Australis respectively. When charged particles from the solar wind reach the Earth's magnetosphere, they spiral along the magnetic field lines towards the North and South poles. If they collide with particles in the Earth's atmosphere, they can cause red or green lights which stretch across a large part of the sky and which is called the aurora. Because this only happens close to the North and South poles, we cannot see the aurorae from South Africa. However, people living in the high Northern latitudes in Canada, Sweden, and Finland, for example, often see the Northern lights.
This simulation shows you the Earth's magnetic field and a compass.

This video provides a summary of the work covered in this chapter.
Khan academy video on magnets

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics - grade 10 [caps 2011]' conversation and receive update notifications?