| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Watch this video to learn about ribosomes. The ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule to start translation of its code into a protein. What happens to the small and large ribosomal subunits at the end of translation?
Translation works because each unique anticodon carries a specific amino acid. The same anticodon carries the same amino acid in virtually all living organisms on earth. This is why gene splicing and genetic engineering work. The complete collection of amino-acid/nucleotide-sequence relationships is called the Genetic Code . However, the Genetic Code uses the complementary mRNA codon sequences rather than the tRNA anticodon sequences to denote the relationship with the amino acid. The Genetic Code is presented in various formats. The two most common are the table format (not shown) and the wheel format shown below ( [link] ).
The genetic code
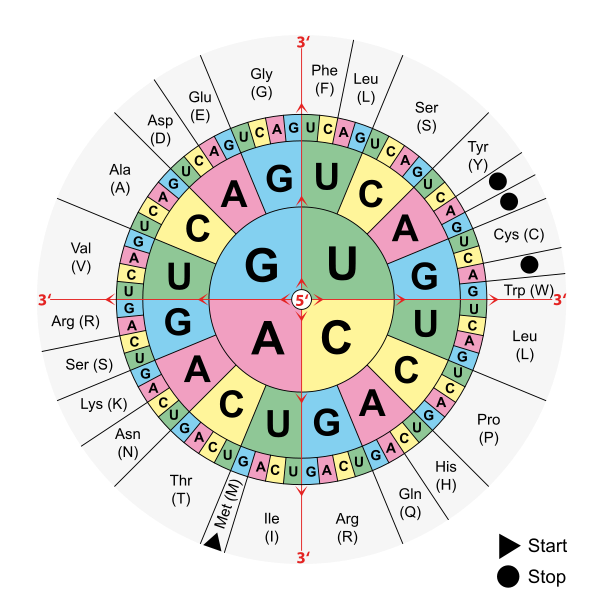
The wheel is read from the center out (in the 5' to 3' direction). It is read by finding the first letter of the codon sequence in the inner most circle, then finding the second letter of the codon sequence from the four choices next to it in the second ring. The process is repeated in the third ring by choosing the third letter of the codon sequence from the four choices next to the second letter. The amino acid associated with the codon is found in the adjacent segment outside the circle.
Notice that four of the codon sequences have special significance. The sequence AUG is the start codon. This tells the ribosome where to start the translation. It also codes for the amino acid methionine. The other three special codon sequences are, UAA, UAG, and UGA. These are the stop codons. When the ribosome encounters these codons it stops the translation and releases the newly formed protein.
Looking at the amino acids around the outside of the wheel you also should notice that while each codon sequence is specific to a single amino acid, the reverse is not true. Most of the amino acids are associated with more than one codon. This redundancy in the Genetic Code can have a significant effect in some circumstances. Point mutations can occur in the DNA where one base is substituted for another. Even though the DNA has a mutation, the sequence now is different, if the resulting mRNA codon still codes for the same amino acid the resulting protein will not change. When this happens it is called a silent mutation .
There are many ways the DNA can be altered by mutation. However, the changes to the original sequence are one of the three generic types:
The effects of the mutation will differ depending on the specifics of each case. The effect generally will fall into one of four categories:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ucd bis2a intro to biology v1.2' conversation and receive update notifications?