| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
[LO 1.2, 2.4]
Take a fresh plant with roots, rinse the roots to remove the soil and carefully examine the roots. Are you able to see the fine, hair-like growths at the tips of the roots? They will be particularly visible on bean plants that you germinate from seeds yourself. These structures are known as root hairs, or radical hairs.
What is the function of a root hair?
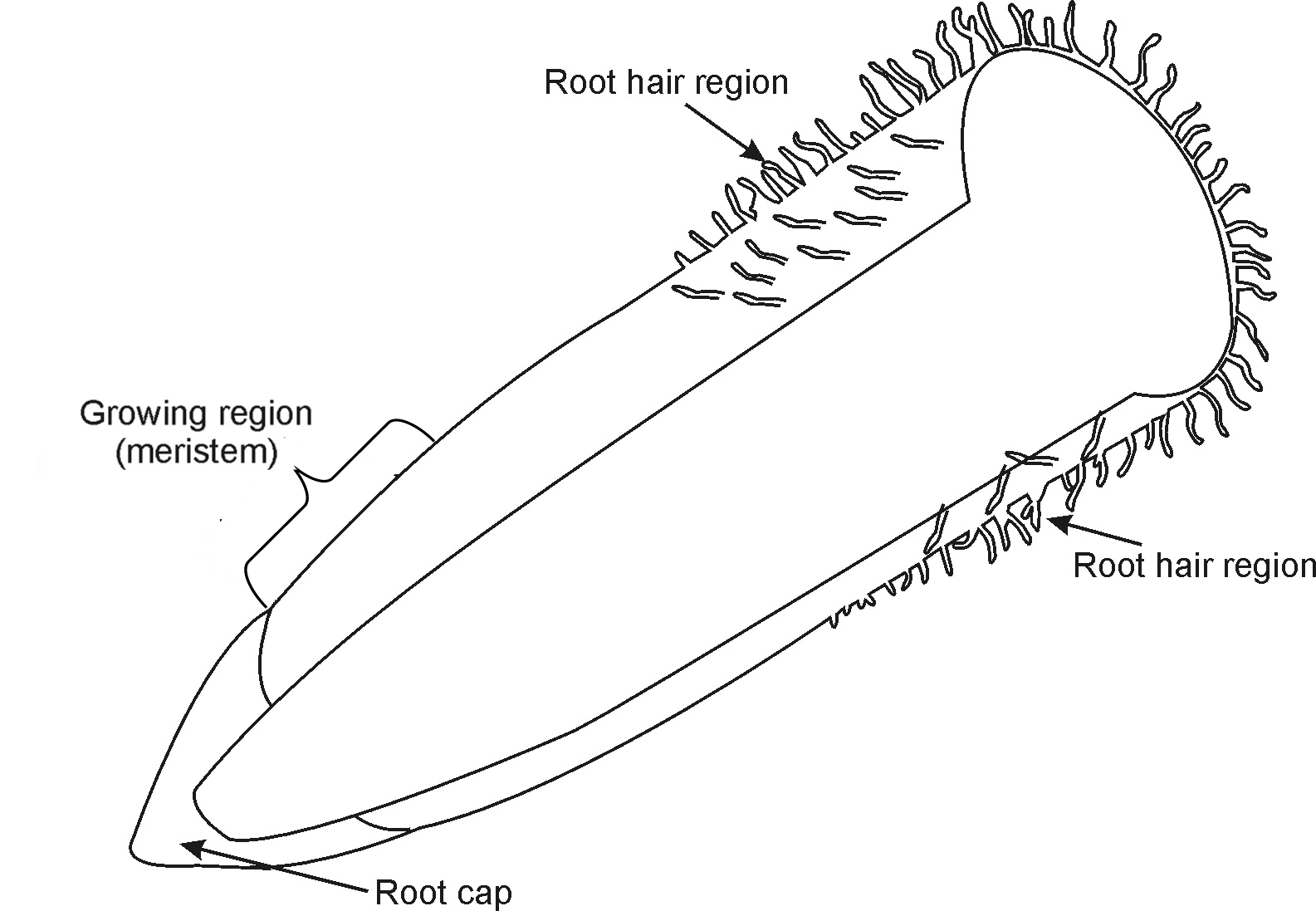
The following is an illustration of the tip of a root:
Assignment 3:
Explain what happens in each of the following regions:
Root hair region:
owing region:
Root tip:
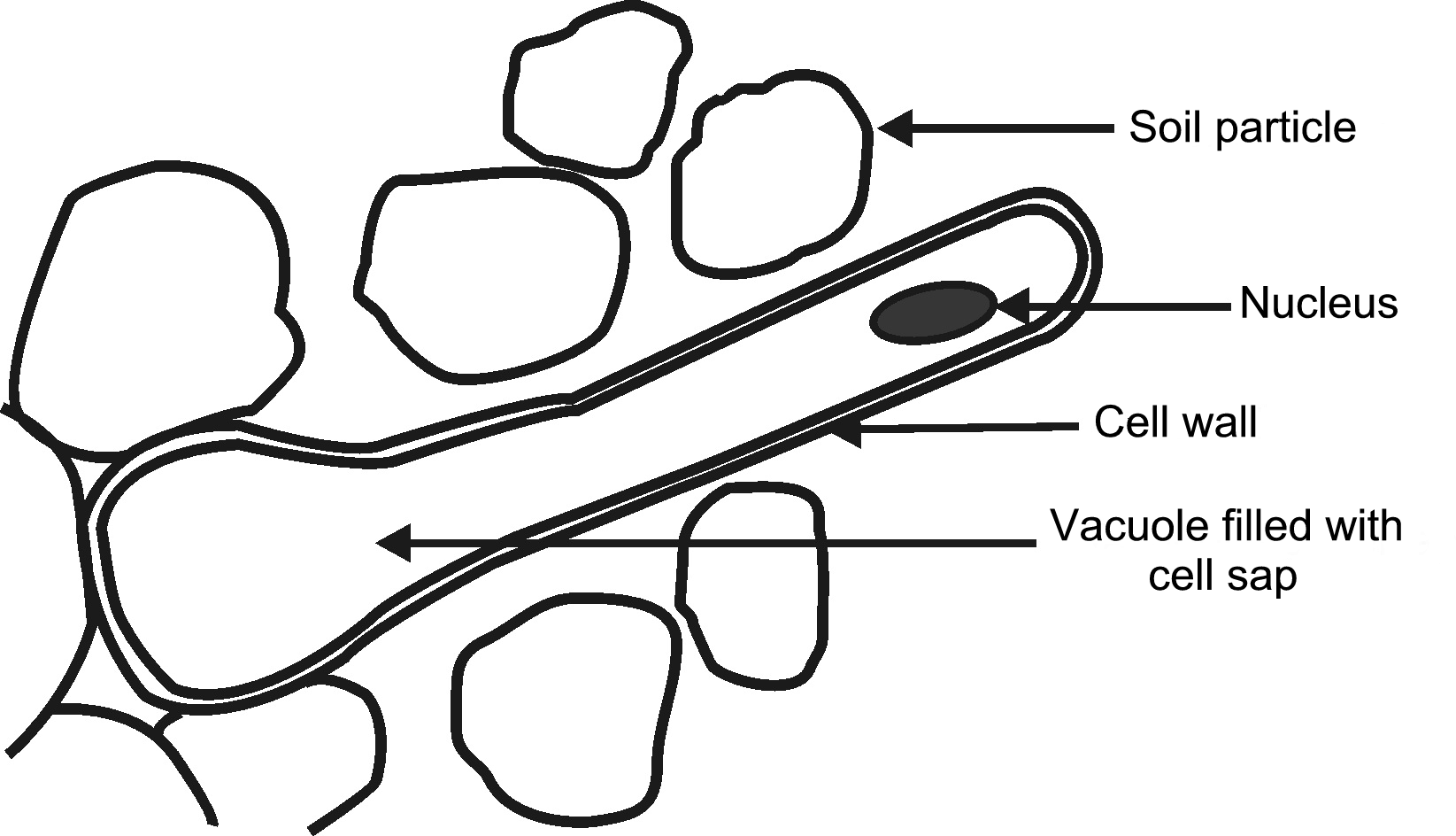
Root hairs consist of special cells on the outer surface of the root right behind the growing region, which increase the surface of the root so that the maximum amount of water and mineral salts can be taken up from the soil.
Assignment 4:
Make a drawing showing the structure of a typical root hair. Provide your drawing with labels and a caption.
The root hair penetrates the small spaces between the particles of soil to suck up the moisture that is trapped between the soil particles. Then it is the function of the next plant organ, namely the plant stem, to conduct the moisture further.
Assessment: Root hairs
Were you able to draw the basic sketch?
[LO 1.2]
LO 1: Scientific investigations:
The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
This is evident when the learner:
LO 2: Constructing Science Knowledge:
The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
This is evident when the learner:
2.4 applies knowledge.
PLANT ORGANS: ROOTS
Activity 1
Assignment 1
A typical plant consists of the PLANT ORGANS :
| Plant organ |
| Root |
| Stem |
| Leaf |
| Flower |
| Above ground or underground |
| Under |
| Above |
| Above |
| Above |
| Main function with regard to the plant | |
| Absorbs water and minerals; anchors the plant. | |
| Bears the leaves and flowers, and fruit, eventually, in a way that exposes each organ correctly. | |
| Photosynthesis | |
| Propagation | |
| Above ground or undergroundMain function with regard to the plant | |
| Root UnderAbsorbs water and minerals; anchors the plant. | |
| Stem AboveBears the leaves and flowers, and fruit, eventually, in a way that exposes each organ correctly. | |
| Leaf AbovePhotosynthesis | |
| Flower AbovePropagation |
Activity 2
Assignment 1
ROOT SYSTEMS
Assignment 2
A taproot system consists of one main root, the taproot, and lateral roots that grow from it.
An adventitious root system consists of equally sized roots that grow from the base of the stem, the adventitious roots .
The life cycle of annuals is completed in a year – they do not need taproots – and they will therefore have an adventitious root system
Trees have a taproot system because they require to be anchored deeply and have to obtain water from deep below the ground.
As adventitious roots grow from stems, they will be of no value for trees that need deep anchoring.
Lateral roots only grow out of other roots.
Main functions of roots:
anchoring
uptake of water
uptake of mineral salts in solution
conducting water to the upper parts of the plant
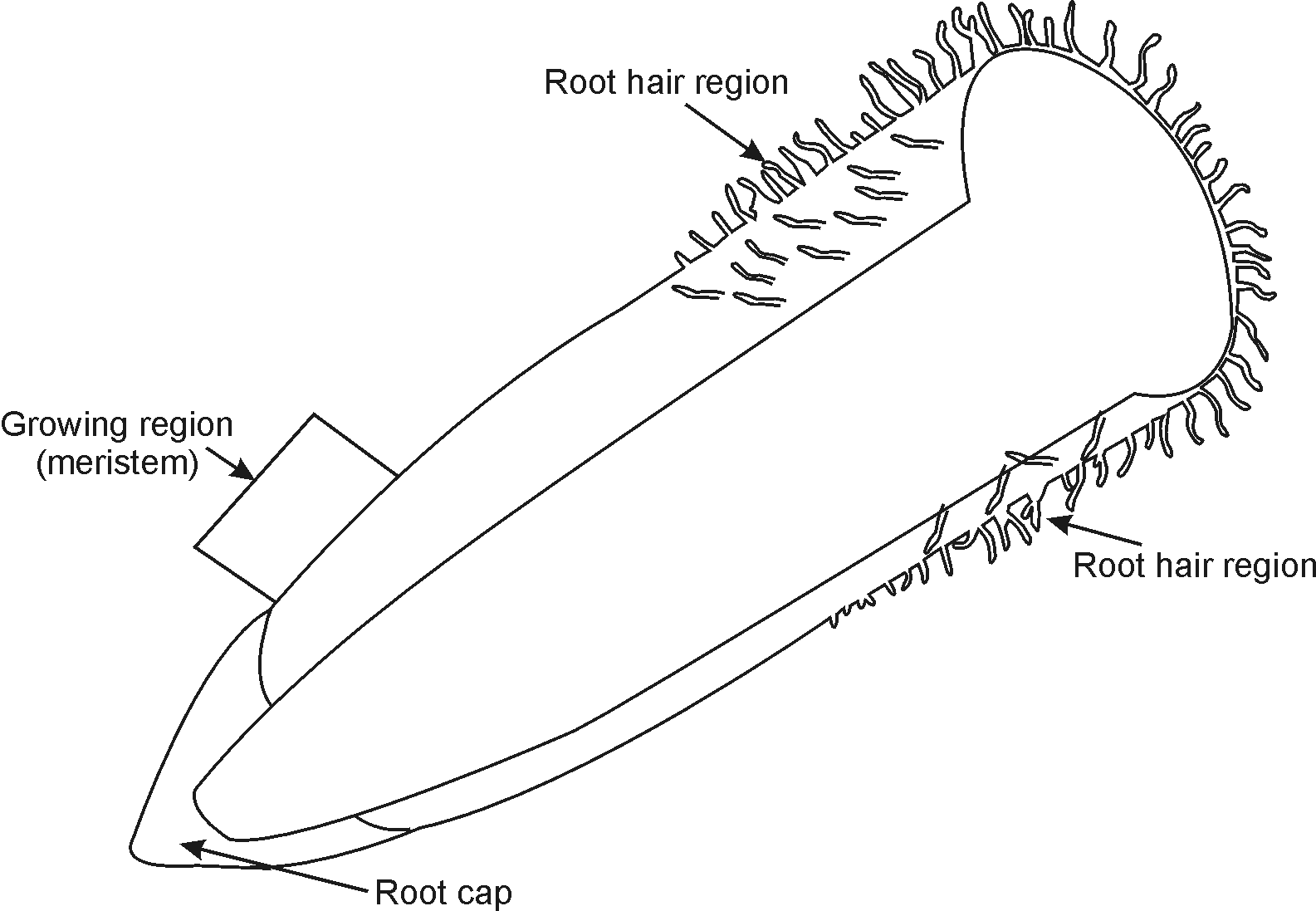
When a root system is investigated, the following structure can be observed:
Assignment 3
Root hair region: region where root hairs develop
Cell lengthening region: region where cells lengthen and differentiate
Cell division region: where cells divide
Meristem: general region where cell division and cell lengthening occur
Root tip: Protects the sensitive foremost growth tip by keeping it slimy to prevent wear.
The srtucture of the root hair is of importance in further studies in Biology.
Assignment 4
This is what we shall focus on next.
Root hair

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?