| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By now you have progressed from the very informal definition of a limit in the introduction of this chapter to the intuitive understanding of a limit. At this point, you should have a very strong intuitive sense of what the limit of a function means and how you can find it. In this section, we convert this intuitive idea of a limit into a formal definition using precise mathematical language. The formal definition of a limit is quite possibly one of the most challenging definitions you will encounter early in your study of calculus; however, it is well worth any effort you make to reconcile it with your intuitive notion of a limit. Understanding this definition is the key that opens the door to a better understanding of calculus.
Before stating the formal definition of a limit, we must introduce a few preliminary ideas. Recall that the distance between two points a and b on a number line is given by
It is also important to look at the following equivalences for absolute value:
With these clarifications, we can state the formal epsilon-delta definition of the limit .
Let be defined for all over an open interval containing a . Let L be a real number. Then
if, for every there exists a such that if then
This definition may seem rather complex from a mathematical point of view, but it becomes easier to understand if we break it down phrase by phrase. The statement itself involves something called a universal quantifier (for every an existential quantifier (there exists a and, last, a conditional statement (if then Let’s take a look at [link] , which breaks down the definition and translates each part.
| Definition | Translation |
|---|---|
| 1. For every | 1. For every positive distance ε from L , |
| 2. there exists a | 2. There is a positive distance from a , |
| 3. such that | 3. such that |
| 4. if then | 4. if x is closer than to a and then is closer than ε to L . |
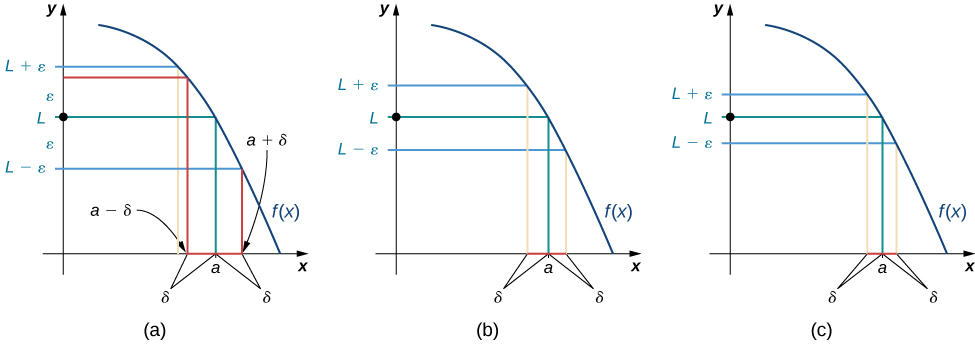
We can get a better handle on this definition by looking at the definition geometrically. [link] shows possible values of for various choices of for a given function a number a , and a limit L at a . Notice that as we choose smaller values of ε (the distance between the function and the limit), we can always find a small enough so that if we have chosen an x value within of a , then the value of is within ε of the limit L .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?