| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
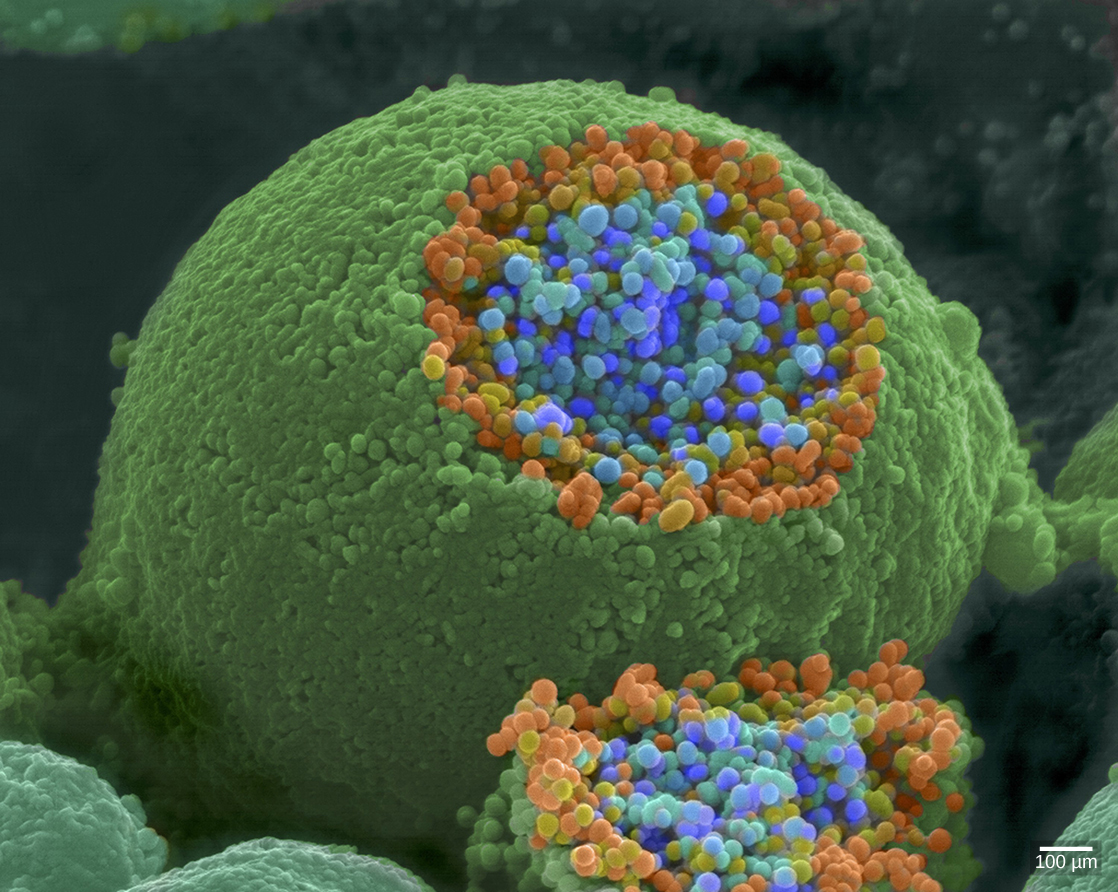
When an action potential reaches the axon terminal it depolarizes the membrane and opens voltage-gated Na + channels. Na + ions enter the cell, further depolarizing the presynaptic membrane. This depolarization causes voltage-gated Ca 2+ channels to open. Calcium ions entering the cell initiate a signaling cascade that causes small membrane-bound vesicles, called synaptic vesicles , containing neurotransmitter molecules to fuse with the presynaptic membrane. Synaptic vesicles are shown in [link] , which is an image from a scanning electron microscope.
Fusion of a vesicle with the presynaptic membrane causes neurotransmitter to be released into the synaptic cleft , the extracellular space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes, as illustrated in [link] . The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptor proteins on the postsynaptic membrane.
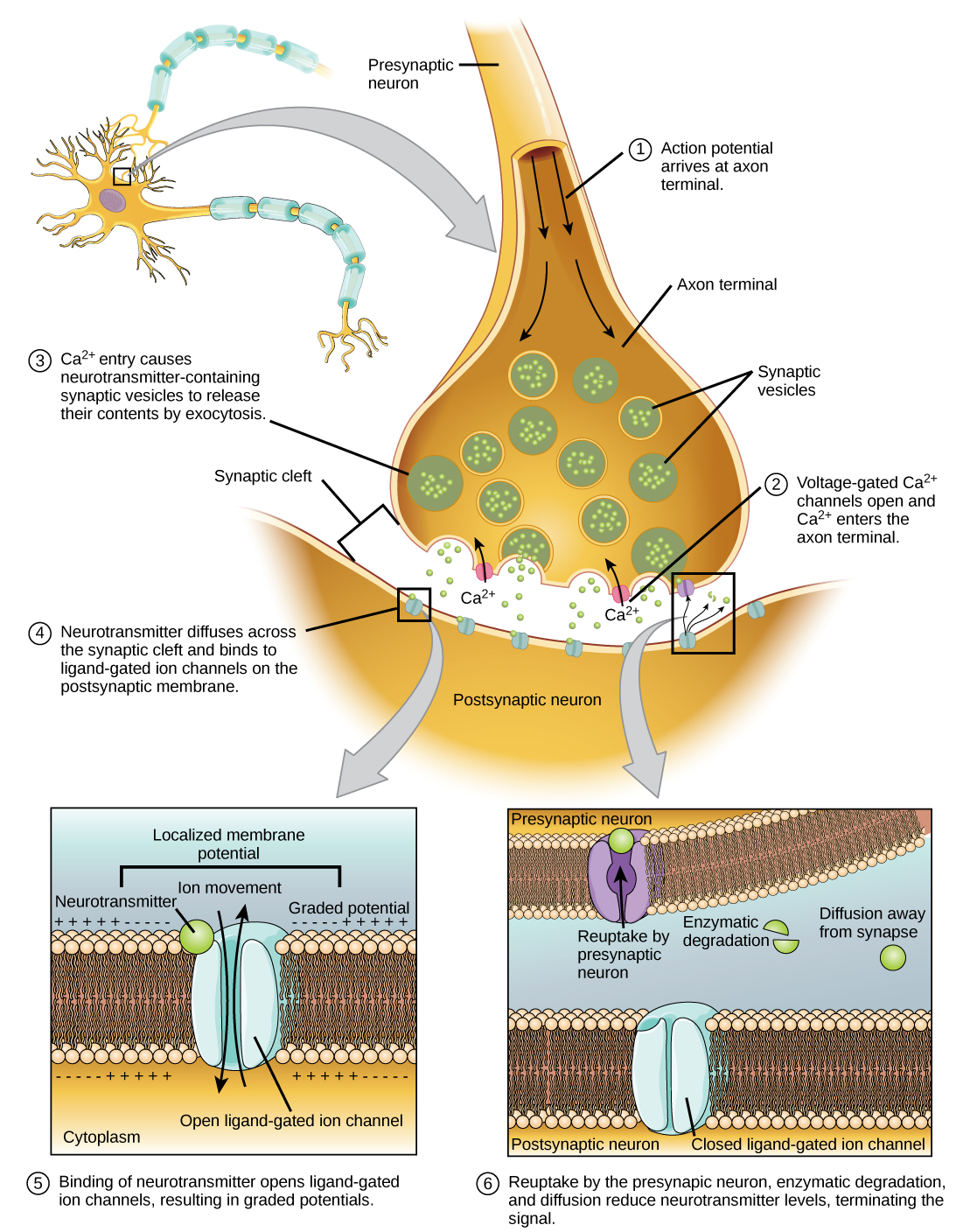
The binding of a specific neurotransmitter causes particular ion channels, in this case chemically-gated channels, on the postsynaptic membrane to open. Neurotransmitters can either have excitatory or inhibitory effects on the postsynaptic membrane, as detailed in [link] . For example, when acetylcholine is released at the synapse between a nerve and muscle (called the neuromuscular junction) by a presynaptic neuron, it causes postsynaptic Na + channels to open. Na + enters the postsynaptic cell and causes the postsynaptic membrane to depolarize. This depolarization is called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) and makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. Release of neurotransmitter at inhibitory synapses causes inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) , a hyperpolarization of the presynaptic membrane. For example, when the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is released from a presynaptic neuron, it binds to and opens Cl - channels. Cl - ions enter the cell and hyperpolarizes the membrane, making the neuron less likely to fire an action potential.
Once neurotransmission has occurred, the neurotransmitter must be removed from the synaptic cleft so the postsynaptic membrane can “reset” and be ready to receive another signal. This can be accomplished in three ways: the neurotransmitter can diffuse away from the synaptic cleft, it can be degraded by enzymes in the synaptic cleft, or it can be recycled (sometimes called reuptake) by the presynaptic neuron. Several drugs act at this step of neurotransmission. For example, some drugs that are given to Alzheimer’s patients work by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme that degrades acetylcholine. This inhibition of the enzyme essentially increases neurotransmission at synapses that release acetylcholine. Once released, the acetylcholine stays in the cleft and can continually bind and unbind to postsynaptic receptors.
| Neurotransmitter Function and Location | ||
|---|---|---|
| Neurotransmitter | Example | Location |
| Acetylcholine | — | CNS and/or PNS |
| Biogenic amine | Dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine | CNS and/or PNS |
| Amino acid | Glycine, glutamate, aspartate, gamma aminobutyric acid | CNS |
| Neuropeptide | Substance P, endorphins | CNS and/or PNS |
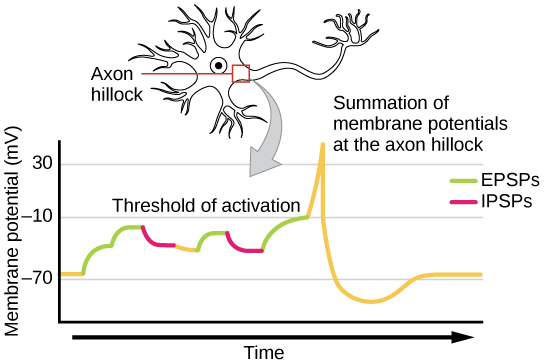
Sometimes a single EPSP is strong enough to induce an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron, but often multiple presynaptic inputs must create EPSPs around the same time for the postsynaptic neuron to be sufficiently depolarized to fire an action potential. This process is called summation and occurs at the axon hillock, as illustrated in [link] . Additionally, one neuron often has inputs from many presynaptic neurons—some excitatory and some inhibitory—so IPSPs can cancel out EPSPs and vice versa. It is the net change in postsynaptic membrane voltage that determines whether the postsynaptic cell has reached its threshold of excitation needed to fire an action potential. Together, synaptic summation and the threshold for excitation act as a filter so that random “noise” in the system is not transmitted as important information.
Neurons have charged membranes because there are different concentrations of ions inside and outside of the cell. Voltage-gated ion channels control the movement of ions into and out of a neuron. When a neuronal membrane is depolarized to at least the threshold of excitation, an action potential is fired. The action potential is then propagated along an axon to the axon terminals. In a chemical synapse, the action potential causes release of neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft. Through binding to postsynaptic receptors, the neurotransmitter can cause excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potentials by depolarizing or hyperpolarizing, respectively, the postsynaptic membrane.
[link] Potassium channel blockers, such as amiodarone and procainamide, which are used to treat abnormal electrical activity in the heart, called cardiac dysrhythmia, impede the movement of K+ through voltage-gated K+ channels. Which part of the action potential would you expect potassium channels to affect?
[link] Potassium channel blockers slow the repolarization phase, but have no effect on depolarization.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?