| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As we mentioned in The Spectra of Stars (and Brown Dwarfs) section, astronomers use the term “metals” to refer to all elements heavier than hydrogen and helium. The fraction of a star’s mass that is composed of these elements is referred to as the star’s metallicity . The metallicity of the Sun, for example, is 0.02, since 2% of the Sun’s mass is made of elements heavier than helium.
Appendix K lists how common each element is in the universe (compared to hydrogen); these estimates are based primarily on investigation of the Sun, which is a typical star. Some very rare elements, however, have not been detected in the Sun. Estimates of the amounts of these elements in the universe are based on laboratory measurements of their abundance in primitive meteorites, which are considered representative of unaltered material condensed from the solar nebula (see the Cosmic Samples and the Origin of the Solar System chapter).
When we measure the spectrum of a star, we determine the wavelength of each of its lines. If the star is not moving with respect to the Sun, then the wavelength corresponding to each element will be the same as those we measure in a laboratory here on Earth. But if stars are moving toward or away from us, we must consider the Doppler effect (see The Doppler Effect section). We should see all the spectral lines of moving stars shifted toward the red end of the spectrum if the star is moving away from us, or toward the blue (violet) end if it is moving toward us ( [link] ). The greater the shift, the faster the star is moving. Such motion, along the line of sight between the star and the observer, is called radial velocity and is usually measured in kilometers per second.
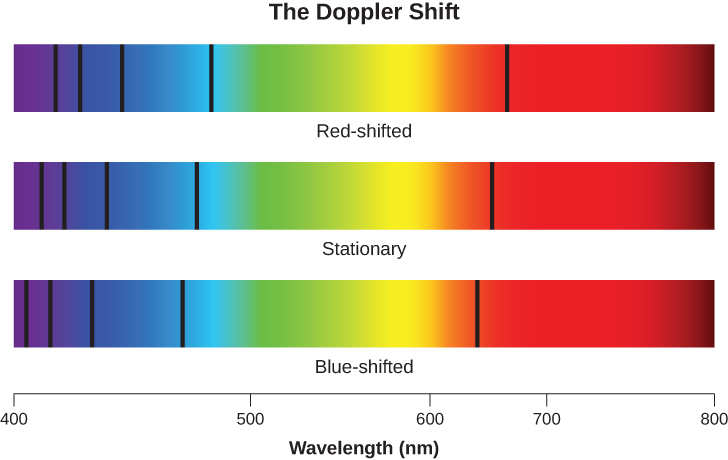
William Huggins , pioneering yet again, in 1868 made the first radial velocity determination of a star. He observed the Doppler shift in one of the hydrogen lines in the spectrum of Sirius and found that this star is moving toward the solar system. Today, radial velocity can be measured for any star bright enough for its spectrum to be observed. As we will see in The Stars: A Celestial Census , radial velocity measurements of double stars are crucial in deriving stellar masses.
There is another type of motion stars can have that cannot be detected with stellar spectra. Unlike radial motion, which is along our line of sight (i.e., toward or away from Earth), this motion, called proper motion , is transverse : that is, across our line of sight. We see it as a change in the relative positions of the stars on the celestial sphere ( [link] ). These changes are very slow. Even the star with the largest proper motion takes 200 years to change its position in the sky by an amount equal to the width of the full Moon, and the motions of other stars are smaller yet.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?