| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
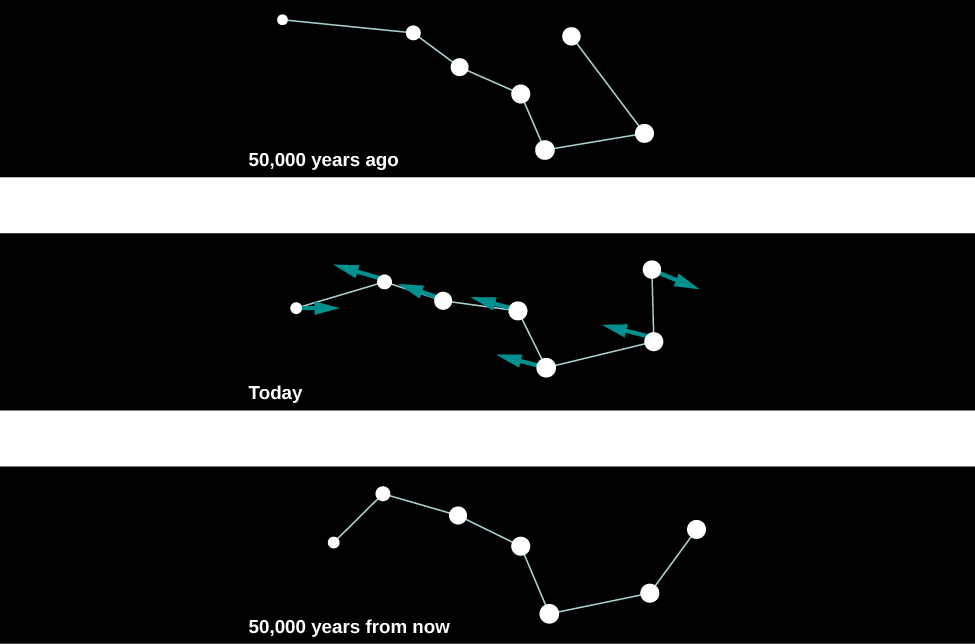
For this reason, with our naked eyes, we do not notice any change in the positions of the bright stars during the course of a human lifetime. If we could live long enough, however, the changes would become obvious. For example, some 50,000 years from now, terrestrial observers will find the handle of the Big Dipper unmistakably more bent than it is now ( [link] ).
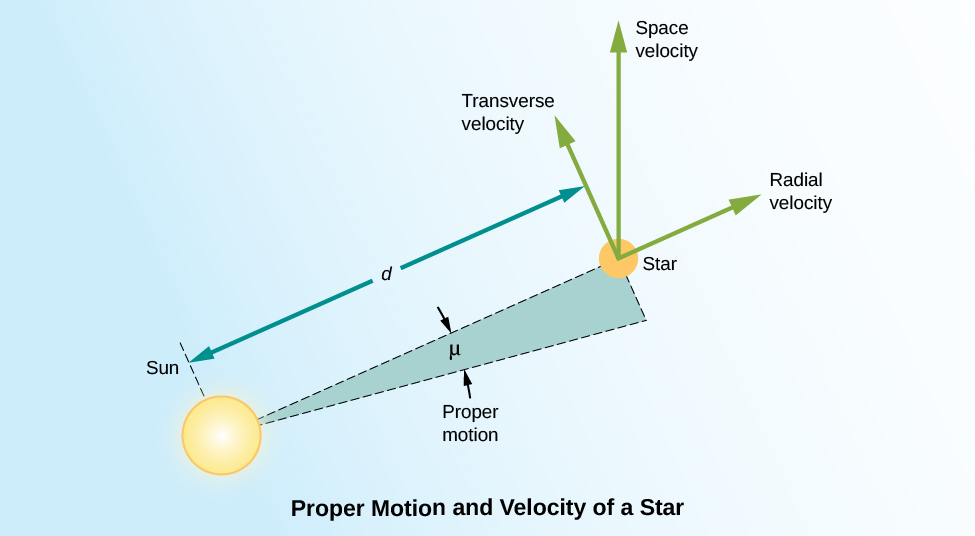
We measure the proper motion of a star in arcseconds (1/3600 of a degree) per year. That is, the measurement of proper motion tells us only by how much of an angle a star has changed its position on the celestial sphere. If two stars at different distances are moving at the same velocity perpendicular to our line of sight, the closer one will show a larger shift in its position on the celestial sphere in a year’s time. As an analogy, imagine you are standing at the side of a freeway. Cars will appear to whiz past you. If you then watch the traffic from a vantage point half a mile away, the cars will move much more slowly across your field of vision. In order to convert this angular motion to a velocity, we need to know how far away the star is.
To know the true space velocity of a star—that is, its total speed and the direction in which it is moving through space relative to the Sun—we must know its radial velocity, proper motion, and distance ( [link] ). A star’s space velocity can also, over time, cause its distance from the Sun to change significantly. Over several hundred thousand years, these changes can be large enough to affect the apparent brightnesses of nearby stars. Today, Sirius , in the constellation Canis Major (the Big Dog) is the brightest star in the sky, but 100,000 years ago, the star Canopus in the constellation Carina (the Keel) was the brightest one. A little over 200,000 years from now, Sirius will have moved away and faded somewhat, and Vega , the bright blue star in Lyra, will take over its place of honor as the brightest star in Earth’s skies.
We can also use the Doppler effect to measure how fast a star rotates. If an object is rotating, then one of its sides is approaching us while the other is receding (unless its axis of rotation happens to be pointed exactly toward us). This is clearly the case for the Sun or a planet; we can observe the light from either the approaching or receding edge of these nearby objects and directly measure the Doppler shifts that arise from the rotation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?