| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An often-debated third type of crime is victimless crime . Crimes are called victimless when the perpetrator is not explicitly harming another person. As opposed to battery or theft, which clearly have a victim, a crime like drinking a beer when someone is twenty years old or selling a sexual act do not result in injury to anyone other than the individual who engages in them, although they are illegal. While some claim acts like these are victimless, others argue that they actually do harm society. Prostitution may foster abuse toward women by clients or pimps. Drug use may increase the likelihood of employee absences. Such debates highlight how the deviant and criminal nature of actions develops through ongoing public discussion.
On the evening of October 3, 2010, a seventeen-year-old boy from the Bronx was abducted by a group of young men from his neighborhood and taken to an abandoned row house. After being beaten, the boy admitted he was gay. His attackers seized his partner and beat him as well. Both victims were drugged, sodomized, and forced to burn one another with cigarettes. When questioned by police, the ringleader of the crime explained that the victims were gay and “looked like [they] liked it” (Wilson and Baker 2010).
Attacks based on a person’s race, religion, or other characteristics are known as hate crimes . Hate crimes in the United States evolved from the time of early European settlers and their violence toward Native Americans. Such crimes weren’t investigated until the early 1900s, when the Ku Klux Klan began to draw national attention for its activities against blacks and other groups. The term “hate crime,” however, didn’t become official until the1980s (Federal Bureau of Investigations 2011).
An average of 195,000 Americans fall victim to hate crimes each year, but fewer than five percent ever report the crime (FBI 2010). The majority of hate crimes are racially motivated, but many are based on religious (especially anti-Semitic) prejudice (FBI 2010). After incidents like the murder of Matthew Shepard in Wyoming in 1998 and the tragic suicide of Rutgers University student Tyler Clementi in 2010, there has been a growing awareness of hate crimes based on sexual orientation.
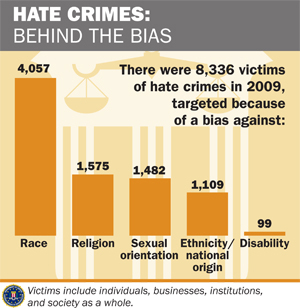
The FBI gathers data from approximately 17,000 law enforcement agencies, and the Uniform Crime Reports (UCR) is the annual publication of this data (FBI 2011). The UCR has comprehensive information from police reports but fails to account for the many crimes that go unreported, often due to victims’ fear, shame, or distrust of the police. The quality of this data is also inconsistent because of differences in approaches to gathering victim data; important details are not always asked for or reported (Cantor and Lynch 2000).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to sociology 2e' conversation and receive update notifications?