| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In 2012, people who worked in the United States spent an average of 56.4 hours per week working (Bureau of Labor Statistics—U.S. Department of Labor, 2013). Sleeping was the only other activity they spent more time on with an average of 61.2 hours per week. The workday is a significant portion of workers’ time and energy. It impacts their lives and their family’s lives in positive and negative physical and psychological ways. Industrial and organizational (I-O) psychology is a branch of psychology that studies how human behavior and psychology affect work and how they are affected by work.
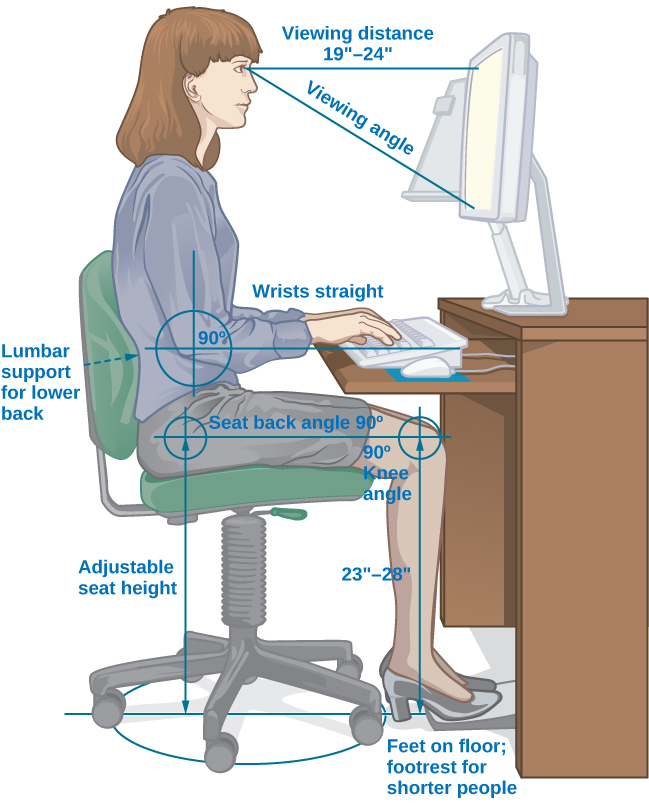
Industrial and organizational psychologists work in four main contexts: academia, government, consulting firms, and business. Most I-O psychologists have a master’s or doctorate degree. The field of I-O psychology can be divided into three broad areas ( [link] and [link] ): industrial, organizational, and human factors. Industrial psychology is concerned with describing job requirements and assessing individuals for their ability to meet those requirements. In addition, once employees are hired, industrial psychology studies and develops ways to train, evaluate, and respond to those evaluations. As a consequence of its concern for candidate characteristics, industrial psychology must also consider issues of legality regarding discrimination in hiring. Organizational psychology is a discipline interested in how the relationships among employees affect those employees and the performance of a business. This includes studying worker satisfaction, motivation, and commitment. This field also studies management, leadership, and organizational culture, as well as how an organization’s structures, management and leadership styles, social norms, and role expectations affect individual behavior. As a result of its interest in worker wellbeing and relationships, organizational psychology also considers the subjects of harassment, including sexual harassment, and workplace violence. Human factors psychology is the study of how workers interact with the tools of work and how to design those tools to optimize workers’ productivity, safety, and health. These studies can involve interactions as straightforward as the fit of a desk, chair, and computer to a human having to sit on the chair at the desk using the computer for several hours each day. They can also include the examination of how humans interact with complex displays and their ability to interpret them accurately and quickly. In Europe, this field is referred to as ergonomics.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?