| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Create a p - n junction and observe the behavior of a simple circuit for forward and reverse bias voltages. Visit this site to learn more about semiconductor diodes.
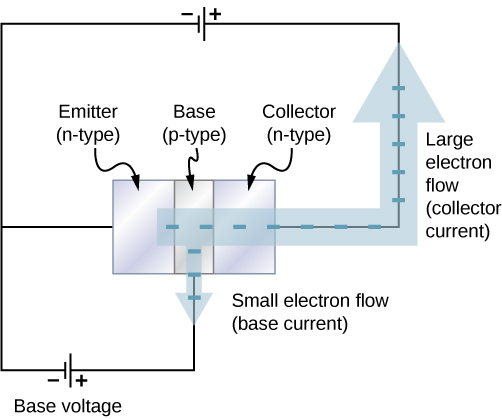
If diodes are one-way valves, transistors are one-way valves that can be carefully opened and closed to control current. A special kind of transistor is a junction transistor. A junction transistor has three parts, including an n -type semiconductor, also called the emitter; a thin p -type semiconductor, which is the base; and another n -type semiconductor, called the collector ( [link] ). When a positive terminal is connected to the p -type layer (the base), a small current of electrons, called the base current flows to the terminal. This causes a large collector current to flow through the collector. The base current can be adjusted to control the large collector current. The current gain is therefore
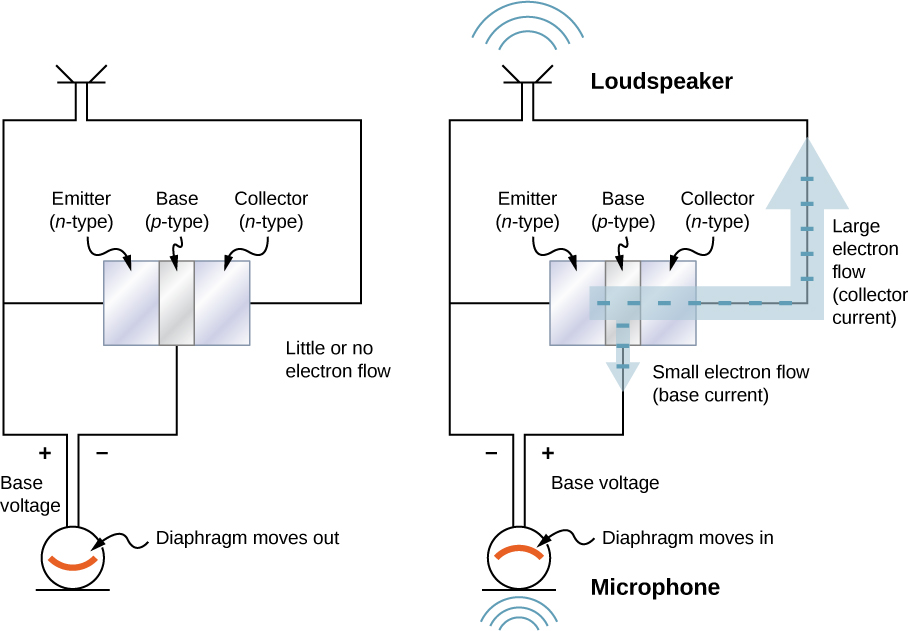
A junction transistor can be used to amplify the voltage from a microphone to drive a loudspeaker. In this application, sound waves cause a diaphragm inside the microphone to move in and out rapidly ( [link] ). When the diaphragm is in the “in” position, a tiny positive voltage is applied to the base of the transistor. This opens the transistor “valve” and allows a large electrical current flow to the loudspeaker. When the diaphragm is in the “out” position, a tiny negative voltage is applied to the base of the transistor, which shuts off the transistor valve so that no current flows to the loudspeaker. This shuts the transistor “valve” off so no current flows to the loudspeaker. In this way, current to the speaker is controlled by the sound waves, and the sound is amplified. Any electric device that amplifies a signal is called an amplifier .
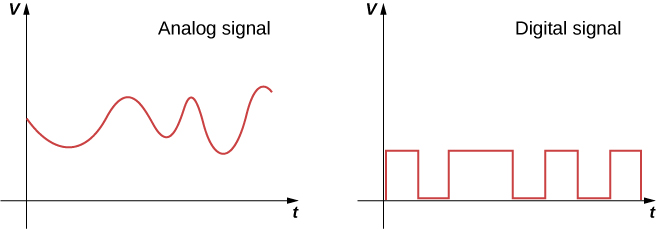
In modern electronic devices, digital signals are used with diodes and transistors to perform tasks such as data manipulation. Electric circuits carry two types of electrical signals: analog and digital ( [link] ). An analog signal varies continuously, whereas a digital signal switches between two fixed voltage values, such as plus 1 volt and zero volts. In digital circuits like those found in computers, a transistor behaves like an on-off switch. The transistor is either on, meaning the valve is completely open, or it is off, meaning the valve is completely closed. Integrated circuits contain vast collections of transistors on a single piece of silicon. They are designed to handle digital signals that represent ones and zeroes, which is also known as binary code. The invention of the ic helped to launch the modern computer revolution.
When p - and n -type materials are joined, why is a uniform electric field generated near the junction?
When p - and n -type materials are joined, why does the depletion layer not grow indefinitely?
The electric field produced by the uncovered ions reduces further diffusion. In equilibrium, the diffusion and drift currents cancel so the net current is zero. Therefore, the resistance of the depletion region is large.
How do you know if a diode is in the forward biased configuration?
Why does the reverse bias configuration lead to a very small current?
The positive terminal is applied to the n -side, which uncovers more ions near the junction (widens the depletion layer), increases the junction voltage difference, and therefore reduces the diffusion of holes across the junction.
What happens in the extreme case that where the n - and p -type materials are heavily doped?
Explain how an audio amplifier works, using the transistor concept.
Sound moves a diaphragm in and out, which varies the input or base current of the transistor circuit. The transistor amplifies this signal ( p-n-p semiconductor). The output or collector current drives a speaker.
Show that for V less than zero,
A p-n diode has a reverse saturation current . It is forward biased so that it has a current of moving through it. What bias voltage is being applied if the temperature is 300 K?
The collector current of a transistor is 3.4 A for a base current of 4.2 mA. What is the current gain?
Applying the positive end of a battery to the p -side and the negative end to the n -side of a p-n junction, the measured current is . Reversing this polarity give a reverse saturation current of . What is the temperature if the bias voltage is 1.2 V?
The base current of a transistor is 4.4 A, and its current gain 1126. What is the collector current?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?