| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Oscillations are found throughout nature, in such things as electromagnetic waves, vibrating molecules, and the gentle back-and-forth sway of a tree branch. In previous chapters, we used Newtonian mechanics to study macroscopic oscillations, such as a block on a spring and a simple pendulum. In this chapter, we begin to study oscillating systems using quantum mechanics. We begin with a review of the classic harmonic oscillator.
A simple harmonic oscillator is a particle or system that undergoes harmonic motion about an equilibrium position, such as an object with mass vibrating on a spring. In this section, we consider oscillations in one-dimension only. Suppose a mass moves back-and-forth along the
x -direction about the equilibrium position, . In classical mechanics, the particle moves in response to a linear restoring force given by where x is the displacement of the particle from its equilibrium position. The motion takes place between two turning points, , where A denotes the amplitude of the motion. The position of the object varies periodically in time with angular frequency which depends on the mass m of the oscillator and on the force constant k of the net force, and can be written as
The total energy E of an oscillator is the sum of its kinetic energy and the elastic potential energy of the force
At turning points , the speed of the oscillator is zero; therefore, at these points, the energy of oscillation is solely in the form of potential energy . The plot of the potential energy U ( x ) of the oscillator versus its position x is a parabola ( [link] ). The potential-energy function is a quadratic function of x , measured with respect to the equilibrium position. On the same graph, we also plot the total energy E of the oscillator, as a horizontal line that intercepts the parabola at . Then the kinetic energy K is represented as the vertical distance between the line of total energy and the potential energy parabola.
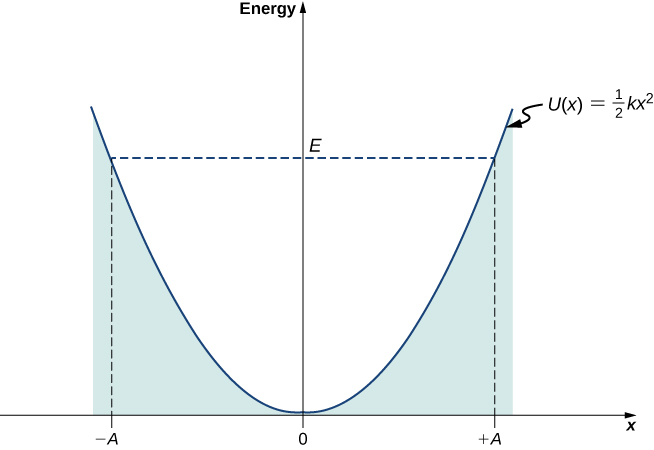
In this plot, the motion of a classical oscillator is confined to the region where its kinetic energy is nonnegative, which is what the energy relation [link] says. Physically, it means that a classical oscillator can never be found beyond its turning points, and its energy depends only on how far the turning points are from its equilibrium position. The energy of a classical oscillator changes in a continuous way. The lowest energy that a classical oscillator may have is zero, which corresponds to a situation where an object is at rest at its equilibrium position. The zero-energy state of a classical oscillator simply means no oscillations and no motion at all (a classical particle sitting at the bottom of the potential well in [link] ). When an object oscillates, no matter how big or small its energy may be, it spends the longest time near the turning points, because this is where it slows down and reverses its direction of motion. Therefore, the probability of finding a classical oscillator between the turning points is highest near the turning points and lowest at the equilibrium position. (Note that this is not a statement of preference of the object to go to lower energy. It is a statement about how quickly the object moves through various regions.)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?