| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nuclear radiation can harm the human body is many other ways as well. For example, high doses of nuclear radiation can cause burns and even hair loss.
Biological effects of nuclear radiation are expressed by many different physical quantities and in many different units. A common unit to express the biological effects of nuclear radiation is the rad or radiation dose unit . One rad is equal to 1/100 of a joule of nuclear energy deposited per kilogram of tissue, written:
For example, if a 50.0-kg person is exposed to nuclear radiation over her entire body and she absorbs 1.00 J, then her whole-body radiation dose is
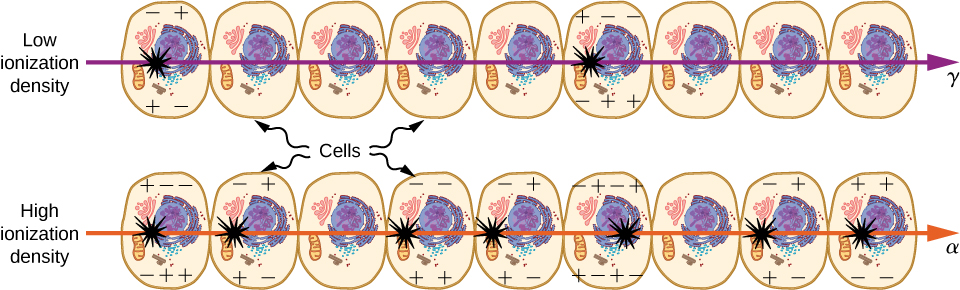
Nuclear radiation damages cells by ionizing atoms in the cells as they pass through the cells ( [link] ). The effects of ionizing radiation depend on the dose in rads, but also on the type of radiation (alpha, beta, gamma, or X-ray) and the type of tissue. For example, if the range of the radiation is small, as it is for rays, then the ionization and the damage created is more concentrated and harder for the organism to repair. To account for such affects, we define the relative biological effectiveness (RBE). Sample RBE values for several types of ionizing nuclear radiation are given in [link] .
| Type and Energy of Radiation | RBE [1] |
|---|---|
| X-rays | 1 |
| rays | 1 |
| rays greater than 32 keV | 1 |
| rays less than 32 keV | 1.7 |
| Neutrons, thermal to slow (<20 keV) | 2–5 |
| Neutrons, fast (1–10 MeV) | 10 (body), 32 (eyes) |
| Protons (1–10 MeV) | 10 (body), 32 (eyes) |
| rays from radioactive decay | 10–20 |
| Heavy ions from accelerators | 10–20 |
A dose unit more closely related to effects in biological tissue is called the roentgen equivalent man (rem) and is defined to be the dose (in rads) multiplied by the relative biological effectiveness (RBE). Thus, if a person had a whole-body dose of 2.00 rad of radiation, the dose in rem would be rem for the whole body. If the person had a whole-body dose of 2.00 rad of radiation, then the dose in rem would be rem for the whole body. The rays would have 20 times the effect on the person than the rays for the same deposited energy. The SI equivalent of the rem, and the more standard term, is the sievert (Sv) is
The RBEs given in [link] are approximate but reflect an understanding of nuclear radiation and its interaction with living tissue. For example, neutrons are known to cause more damage than rays, although both are neutral and have large ranges, due to secondary radiation. Any dose less than 100 mSv (10 rem) is called a low dose , 0.1 Sv to 1 Sv (10 to 100 rem) is called a moderate dose , and anything greater than 1 Sv (100 rem) is called a high dose . It is difficult to determine if a person has been exposed to less than 10 mSv.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?