| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Check Your Understanding A closely wound coil has a radius of 4.0 cm, 50 turns, and a total resistance of . At what rate must a magnetic field perpendicular to the face of the coil change in order to produce Joule heating in the coil at a rate of 2.0 mW?
1.1 T/s
A stationary coil is in a magnetic field that is changing with time. Does the emf induced in the coil depend on the actual values of the magnetic field?
The emf depends on the rate of change of the magnetic field.
In Faraday’s experiments, what would be the advantage of using coils with many turns?
A copper ring and a wooden ring of the same dimensions are placed in magnetic fields so that there is the same change in magnetic flux through them. Compare the induced electric fields and currents in the rings.
Both have the same induced electric fields; however, the copper ring has a much higher induced emf because it conducts electricity better than the wooden ring.
Discuss the factors determining the induced emf in a closed loop of wire.
(a) Does the induced emf in a circuit depend on the resistance of the circuit? (b) Does the induced current depend on the resistance of the circuit?
a. no; b. yes
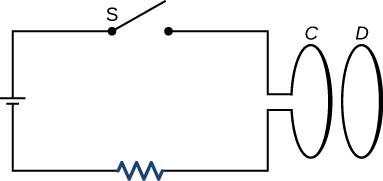
How would changing the radius of loop D shown below affect its emf, assuming C and D are much closer together compared to their radii?
Can there be an induced emf in a circuit at an instant when the magnetic flux through the circuit is zero?
As long as the magnetic flux is changing from positive to negative or negative to positive, there could be an induced emf.
Does the induced emf always act to decrease the magnetic flux through a circuit?
How would you position a flat loop of wire in a changing magnetic field so that there is no induced emf in the loop?
Position the loop so that the field lines run perpendicular to the area vector or parallel to the surface.
The normal to the plane of a single-turn conducting loop is directed at an angle to a spatially uniform magnetic field It has a fixed area and orientation relative to the magnetic field. Show that the emf induced in the loop is given by where A is the area of the loop.
A 50-turn coil has a diameter of 15 cm. The coil is placed in a spatially uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.50 T so that the face of the coil and the magnetic field are perpendicular. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in the coil if the magnetic field is reduced to zero uniformly in (a) 0.10 s, (b) 1.0 s, and (c) 60 s.
Repeat your calculations of the preceding problem’s time of 0.1 s with the plane of the coil making an angle of (a) (b) and (c) with the magnetic field.
a. 3.8 V; b. 2.2 V; c. 0 V
A square loop whose sides are 6.0-cm long is made with copper wire of radius 1.0 mm. If a magnetic field perpendicular to the loop is changing at a rate of 5.0 mT/s, what is the current in the loop?
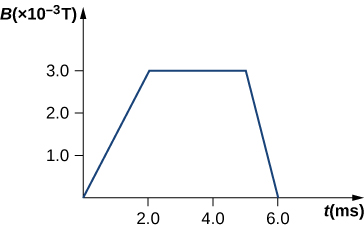
The magnetic field through a circular loop of radius 10.0 cm varies with time as shown below. The field is perpendicular to the loop. Plot the magnitude of the induced emf in the loop as a function of time.
The accompanying figure shows a single-turn rectangular coil that has a resistance of The magnetic field at all points inside the coil varies according to where and What is the current induced in the coil at (a) , (b) 0.002 s, (c) 2.0 s?
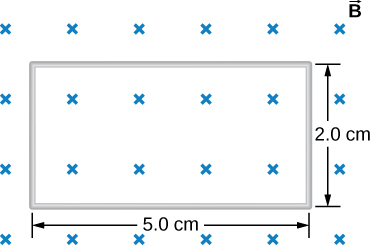
How would the answers to the preceding problem change if the coil consisted of 20 closely spaced turns?
Each answer is 20 times the previously given answers.
A long solenoid with turns per centimeter has a cross-sectional area of and carries a current of 0.25 A. A coil with five turns encircles the solenoid. When the current through the solenoid is turned off, it decreases to zero in 0.050 s. What is the average emf induced in the coil?
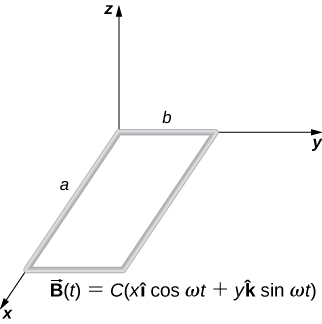
A rectangular wire loop with length a and width b lies in the xy -plane, as shown below. Within the loop there is a time-dependent magnetic field given by , with in tesla. Determine the emf induced in the loop as a function of time.
The magnetic field perpendicular to a single wire loop of diameter 10.0 cm decreases from 0.50 T to zero. The wire is made of copper and has a diameter of 2.0 mm and length 1.0 cm. How much charge moves through the wire while the field is changing?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?