| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
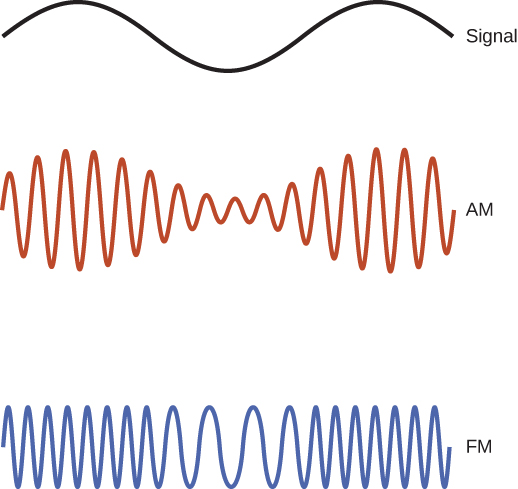
In order to use an electromagnetic wave to transmit information, the amplitude, frequency, or phase of the wave is modulated , or varied in a controlled way that encodes the intended information into the wave. In AM radio transmission, the amplitude of the wave is modulated to mimic the vibrations of the sound being conveyed. Fourier’s theorem implies that the modulated AM wave amounts to a superposition of waves covering some narrow frequency range. Each AM station is assigned a specific carrier frequency that, by international agreement, is allowed to vary by . In FM radio transmission, the frequency of the wave is modulated to carry this information, as illustrated in [link] , and the frequency of each station is allowed to use 100 kHz on each side of its carrier frequency. The electromagnetic wave produces a current in a receiving antenna, and the radio or television processes the signal to produce the sound and any image. The higher the frequency of the radio wave used to carry the data, the greater the detailed variation of the wave that can be carried by modulating it over each time unit, and the more data that can be transmitted per unit of time. The assigned frequencies for AM broadcasting are 540 to 1600 kHz, and for FM are 88 MHz to108 MHz.
Cell phone conversations, and television voice and video images are commonly transmitted as digital data, by converting the signal into a sequence of binary ones and zeros. This allows clearer data transmission when the signal is weak, and allows using computer algorithms to compress the digital data to transmit more data in each frequency range. Computer data as well is transmitted as a sequence of binary ones and zeros, each one or zero constituting one bit of data.
Microwaves are the highest-frequency electromagnetic waves that can be produced by currents in macroscopic circuits and devices. Microwave frequencies range from about to nearly . Their high frequencies correspond to short wavelengths compared with other radio waves—hence the name “microwave.” Microwaves also occur naturally as the cosmic background radiation left over from the origin of the universe. Along with other ranges of electromagnetic waves, they are part of the radiation that any object above absolute zero emits and absorbs because of thermal agitation , that is, from the thermal motion of its atoms and molecules.
Most satellite-transmitted information is carried on microwaves . Radar is a common application of microwaves. By detecting and timing microwave echoes, radar systems can determine the distance to objects as diverse as clouds, aircraft, or even the surface of Venus.
Microwaves of 2.45 GHz are commonly used in microwave ovens. The electrons in a water molecule tend to remain closer to the oxygen nucleus than the hydrogen nuclei ( [link] ). This creates two separated centers of equal and opposite charges, giving the molecule a dipole moment (see Electric Field ). The oscillating electric field of the microwaves inside the oven exerts a torque that tends to align each molecule first in one direction and then in the other, with the motion of each molecule coupled to others around it. This pumps energy into the continual thermal motion of the water to heat the food. The plate under the food contains no water, and remains relatively unheated.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?