| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Earlier we discussed, and calculated, the electric field of a dipole: two equal and opposite charges that are “close” to each other. (In this context, “close” means that the distance d between the two charges is much, much less than the distance of the field point P , the location where you are calculating the field.) Let’s now consider what happens to a dipole when it is placed in an external field . We assume that the dipole is a permanent dipole ; it exists without the field, and does not break apart in the external field.
For now, we deal with only the simplest case: The external field is uniform in space. Suppose we have the situation depicted in [link] , where we denote the distance between the charges as the vector pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge. The forces on the two charges are equal and opposite, so there is no net force on the dipole. However, there is a torque:
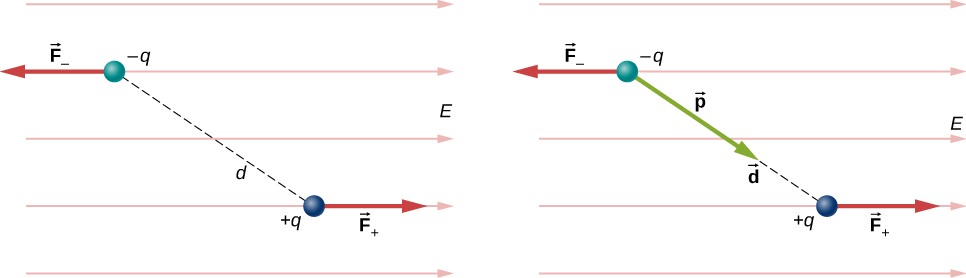
The quantity (the magnitude of each charge multiplied by the vector distance between them) is a property of the dipole; its value, as you can see, determines the torque that the dipole experiences in the external field. It is useful, therefore, to define this product as the so-called dipole moment of the dipole:
We can therefore write
Recall that a torque changes the angular velocity of an object, the dipole, in this case. In this situation, the effect is to rotate the dipole (that is, align the direction of so that it is parallel to the direction of the external field.
Neutral atoms are, by definition, electrically neutral; they have equal amounts of positive and negative charge. Furthermore, since they are spherically symmetrical, they do not have a “built-in” dipole moment the way most asymmetrical molecules do. They obtain one, however, when placed in an external electric field, because the external field causes oppositely directed forces on the positive nucleus of the atom versus the negative electrons that surround the nucleus. The result is a new charge distribution of the atom, and therefore, an induced dipole moment ( [link] ).
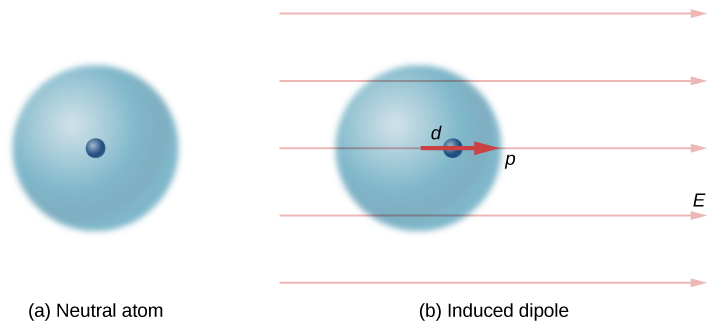
An important fact here is that, just as for a rotated polar molecule, the result is that the dipole moment ends up aligned parallel to the external electric field. Generally, the magnitude of an induced dipole is much smaller than that of an inherent dipole. For both kinds of dipoles, notice that once the alignment of the dipole (rotated or induced) is complete, the net effect is to decrease the total electric field in the regions outside the dipole charges ( [link] ). By “outside” we mean further from the charges than they are from each other. This effect is crucial for capacitors, as you will see in Capacitance .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?