| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
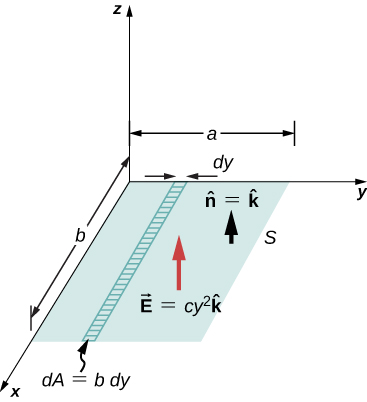
Check Your Understanding If the electric field in [link] is what is the flux through the rectangular area?
Discuss how would orient a planar surface of area A in a uniform electric field of magnitude to obtain (a) the maximum flux and (b) the minimum flux through the area.
a. If the planar surface is perpendicular to the electric field vector, the maximum flux would be obtained. b. If the planar surface were parallel to the electric field vector, the minimum flux would be obtained.
What are the maximum and minimum values of the flux in the preceding question?
The net electric flux crossing a closed surface is always zero. True or false?
true
The net electric flux crossing an open surface is never zero. True or false?
A uniform electric field of magnitude is perpendicular to a square sheet with sides 2.0 m long. What is the electric flux through the sheet?
Calculate the flux through the sheet of the previous problem if the plane of the sheet is at an angle of to the field. Find the flux for both directions of the unit normal to the sheet.
electric field in direction of unit normal; electric field opposite to unit normal
Find the electric flux through a rectangular area between two parallel plates where there is a constant electric field of 30 N/C for the following orientations of the area: (a) parallel to the plates, (b) perpendicular to the plates, and (c) the normal to the area making a angle with the direction of the electric field. Note that this angle can also be given as
The electric flux through a square-shaped area of side 5 cm near a large charged sheet is found to be when the area is parallel to the plate. Find the charge density on the sheet.
Two large rectangular aluminum plates of area face each other with a separation of 3 mm between them. The plates are charged with equal amount of opposite charges, . The charges on the plates face each other. Find the flux through a circle of radius 3 cm between the plates when the normal to the circle makes an angle of with a line perpendicular to the plates. Note that this angle can also be given as
A square surface of area is in a space of uniform electric field of magnitude . The amount of flux through it depends on how the square is oriented relative to the direction of the electric field. Find the electric flux through the square, when the normal to it makes the following angles with electric field: (a) , (b) , and (c) . Note that these angles can also be given as .
a.
b.
; c.
A vector field is pointed along the z -axis, (a) Find the flux of the vector field through a rectangle in the xy -plane between and . (b) Do the same through a rectangle in the yz -plane between and . (Leave your answer as an integral.)
Consider the uniform electric field What is its electric flux through a circular area of radius 2.0 m that lies in the xy -plane?
Repeat the previous problem, given that the circular area is (a) in the yz -plane and (b) above the xy- plane.
An infinite charged wire with charge per unit length lies along the central axis of a cylindrical surface of radius r and length l . What is the flux through the surface due to the electric field of the charged wire?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?