| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A capacitor is a device used to store electrical charge and electrical energy. It consists of at least two electrical conductors separated by a distance. (Note that such electrical conductors are sometimes referred to as “electrodes,” but more correctly, they are “capacitor plates.”) The space between capacitors may simply be a vacuum, and, in that case, a capacitor is then known as a “vacuum capacitor.” However, the space is usually filled with an insulating material known as a dielectric . (You will learn more about dielectrics in the sections on dielectrics later in this chapter.) The amount of storage in a capacitor is determined by a property called capacitance , which you will learn more about a bit later in this section.
Capacitors have applications ranging from filtering static from radio reception to energy storage in heart defibrillators. Typically, commercial capacitors have two conducting parts close to one another but not touching, such as those in [link] . Most of the time, a dielectric is used between the two plates. When battery terminals are connected to an initially uncharged capacitor, the battery potential moves a small amount of charge of magnitude Q from the positive plate to the negative plate. The capacitor remains neutral overall, but with charges and residing on opposite plates.
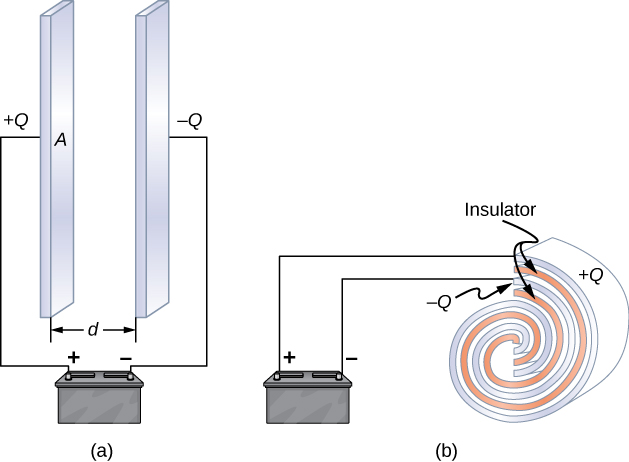
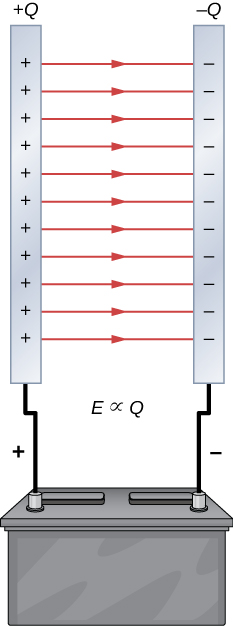
A system composed of two identical parallel-conducting plates separated by a distance is called a parallel-plate capacitor ( [link] ). The magnitude of the electrical field in the space between the parallel plates is , where denotes the surface charge density on one plate (recall that is the charge Q per the surface area A ). Thus, the magnitude of the field is directly proportional to Q .
Capacitors with different physical characteristics (such as shape and size of their plates) store different amounts of charge for the same applied voltage V across their plates. The capacitance C of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the maximum charge Q that can be stored in a capacitor to the applied voltage V across its plates. In other words, capacitance is the largest amount of charge per volt that can be stored on the device:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?