| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As we showed in the preceding section, the net electric force on a test charge is the vector sum of all the electric forces acting on it, from all of the various source charges, located at their various positions. But what if we use a different test charge, one with a different magnitude, or sign, or both? Or suppose we have a dozen different test charges we wish to try at the same location? We would have to calculate the sum of the forces from scratch. Fortunately, it is possible to define a quantity, called the electric field , which is independent of the test charge. It only depends on the configuration of the source charges, and once found, allows us to calculate the force on any test charge.
Suppose we have N source charges located at positions , applying N electrostatic forces on a test charge Q . The net force on Q is (see [link] )
We can rewrite this as
where
or, more compactly,
This expression is called the electric field at position of the N source charges. Here, P is the location of the point in space where you are calculating the field and is relative to the positions of the source charges ( [link] ). Note that we have to impose a coordinate system to solve actual problems.
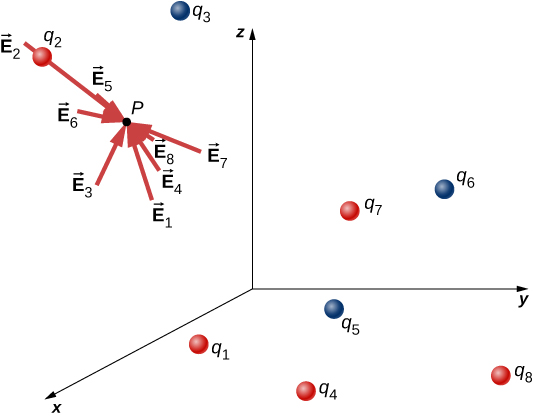
Notice that the calculation of the electric field makes no reference to the test charge. Thus, the physically useful approach is to calculate the electric field and then use it to calculate the force on some test charge later, if needed. Different test charges experience different forces [link] , but it is the same electric field [link] . That being said, recall that there is no fundamental difference between a test charge and a source charge; these are merely convenient labels for the system of interest. Any charge produces an electric field; however, just as Earth’s orbit is not affected by Earth’s own gravity, a charge is not subject to a force due to the electric field it generates. Charges are only subject to forces from the electric fields of other charges.
In this respect, the electric field of a point charge is similar to the gravitational field of Earth; once we have calculated the gravitational field at some point in space, we can use it any time we want to calculate the resulting force on any mass we choose to place at that point. In fact, this is exactly what we do when we say the gravitational field of Earth (near Earth’s surface) has a value of and then we calculate the resulting force (i.e., weight) on different masses. Also, the general expression for calculating at arbitrary distances from the center of Earth (i.e., not just near Earth’s surface) is very similar to the expression for : , where G is a proportionality constant, playing the same role for as does for . The value of is calculated once and is then used in an endless number of problems.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?