| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Eutrophication is the enrichment of an ecosystem with chemical nutrients, normally by compounds that contain nitrogen or phosphorus. Eutrophication is considered a form of pollution because it promotes plant growth, favoring certain species over others. In aquatic environments, the rapid growth of certain types of plants can disrupt the normal functioning of an ecosystem, causing a variety of problems. Human society is impacted as well because eutrophication can decrease the resource value of rivers, lakes, and estuaries making recreational activities less enjoyable. Health-related problems can also occur if eutrophic conditions interfere with the treatment of drinking water.
Eutrophication refers to an increase in chemical nutrients in an ecosystem. These chemical nutrients usually contain nitrogen or phosphorus.
In some cases, eutrophication can be a natural process that occurs very slowly over time. However, it can also be accelerated by certain human activities. Agricultural runoff, when excess fertilisers are washed off fields and into water, and sewage are two of the major causes of eutrophication. There are a number of impacts of eutrophication.
South Africa's Department of Water Affairs and Forestry has a 'National Eutrophication Monitoring Programme' which was set up to monitor eutrophication in impoundments such as dams, where no monitoring was taking place.
Despite the impacts, there are a number of ways of preventing eutrophication from taking place. Cleanup measures can directly remove the excess nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus from the water. Creating buffer zones near farms, roads and rivers can also help. These act as filters and cause nutrients and sediments to be deposited there instead of in the aquatic system. Laws relating to the treatment and discharge of sewage can also help to control eutrophication. A final possible intervention is nitrogen testing and modeling . By assessing exactly how much fertiliser is needed by crops and other plants, farmers can make sure that they only apply just enough fertiliser. This means that there is no excess to run off into neighbouring streams during rain. There is also a cost benefit for the farmer.
In many cases, the damage from eutrophication is already done. In groups, do the following:
Why we need fertilisers
There is likely to be a gap between food production and demand in several parts of the world by 2020. Demand is influenced by population growth and urbanisation, as well as income levels and changes in dietary preferences.
The facts are as follows:
Conclusion: Fertilisers are needed!
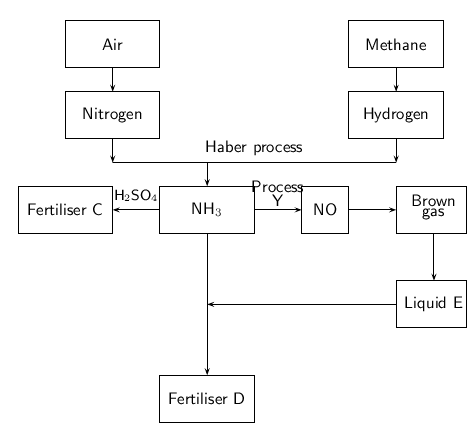
The flow diagram below shows the main steps in the industrial preparation of two important solid fertilisers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?