| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Molecule | Difference in electronegativity between atoms | Non-polar/polar covalent bond | Polar/non-polar molecule |
| H O | |||
| HBr | |||
| F | |||
| CH |
You will remember that when atoms bond, electrons are either shared or they are transferred between the atoms that are bonding. In covalent bonding, electrons are shared between the atoms. There is another type of bonding, where electrons are transferred from one atom to another. This is called ionic bonding .
Ionic bonding takes place when the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms is more than 1.7. This usually happens when a metal atom bonds with a non-metal atom. When the difference in electronegativity is large, one atom will attract the shared electron pair much more strongly than the other, causing electrons to be transferred from one atom to the other.
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond based on the electrostatic forces between two oppositely-charged ions. When ionic bonds form, a metal donates one or more electrons, due to having a low electronegativity, to form a positive ion or cation. The non-metal atom has a high electronegativity, and therefore readily gains electrons to form a negative ion or anion. The two ions are then attracted to each other by electrostatic forces.
Example 1:
In the case of NaCl, the difference in electronegativity is 2.1. Sodium has only one valence electron, while chlorine has seven. Because the electronegativity of chlorine is higher than the electronegativity of sodium, chlorine will attract the valence electron of the sodium atom very strongly. This electron from sodium is transferred to chlorine. Sodium loses an electron and forms a ion. Chlorine gains an electron and forms a ion. The attractive force between the positive and negative ion holds the molecule together.
The balanced equation for the reaction is:
This can be represented using Lewis notation:
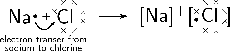
Example 2:
Another example of ionic bonding takes place between magnesium (Mg) and oxygen (O) to form magnesium oxide (MgO). Magnesium has two valence electrons and an electronegativity of 1.2, while oxygen has six valence electrons and an electronegativity of 3.5. Since oxygen has a higher electronegativity, it attracts the two valence electrons from the magnesium atom and these electrons are transferred from the magnesium atom to the oxygen atom. Magnesium loses two electrons to form , and oxygen gains two electrons to form . The attractive force between the oppositely charged ions is what holds the molecule together.
The balanced equation for the reaction is:
Because oxygen is a diatomic molecule, two magnesium atoms will be needed to combine with one oxygen molecule (which has two oxygen atoms) to produce two molecules of magnesium oxide (MgO).
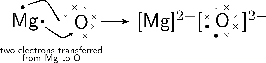
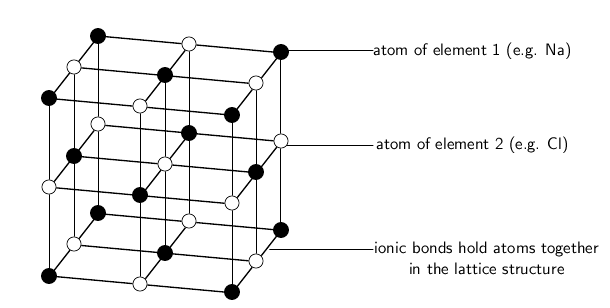
Ionic substances are actually a combination of lots of ions bonded together into a giant molecule. The arrangement of ions in a regular,geometric structure is called a crystal lattice . So in fact NaCl does not contain one Na and one Cl ion, but rather a lot ofthese two ions arranged in a crystal lattice where the ratio of Na to Cl ions is 1:1. The structure of a crystal lattice is shown in [link] .
Ionic compounds have a number of properties:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?