| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The above examples all show single covalent bonds , where only one pair of electrons is shared between the same two atoms . If two pairs of electrons are shared between the same two atoms, this is called a double bond . A triple bond is formed if three pairs of electrons are shared.
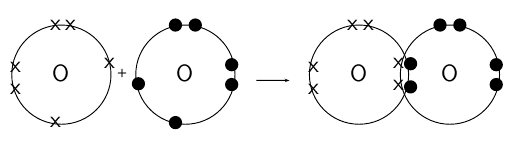
How do oxygen atoms bond covalently to form an oxygen molecule?
Each oxygen atom has 8 electrons, and their electron configuration is 1s 2s 2p .
Each oxygen atom has 6 valence electrons, meaning that each atom has 2 unpaired electrons.
Each oxygen atom needs two more electrons to complete its valence energy shell. Therefore two pairs of electrons must be shared between the two oxygen atoms so that both valence shells are full. Notice that the two electron pairs are being shared between the same two atoms, and so we call this a double bond ( [link] ).
You will have noticed in the above examples that the number of electrons that are involved in bonding varies between atoms. We say that the valency of the atoms is different.
The number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom which are able to be used to form bonds with other atoms.
In the first example, the valency of both hydrogen and chlorine is one, therefore there is a single covalent bond between these two atoms. In the second example, nitrogen has a valency of three and hydrogen has a valency of one. This means that three hydrogen atoms will need to bond with a single nitrogen atom. There are three single covalent bonds in a molecule of ammonia. In the third example, the valency of oxygen is two. This means that each oxygen atom will form two bonds with another atom. Since there is only one other atom in a molecule of O , a double covalent bond is formed between these two atoms.
| Element | No. of valence electrons | No. of electrons needed to fill outer shell | Valency |
| F | |||
| Ar | |||
| C | |||
| N | |||
| O |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?