| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In "Nuclear structure and stability" , we discussed that when a nucleus is unstable it can emit particles and energy. This process is called radioactive decay .
Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting particles or electromagnetic waves. These emitted particles or electromagnetic waves are called radiation .
When a nucleus undergoes radioactive decay, it emits radiation and the nucleus is said to be radioactive. We are exposed to small amounts of radiation all the time. Even the rocks around us emit radiation! However some elements are far more radioactive than others. Even within a single element, there may be some isotopes that are more radioactive than others simply because they contain a larger number of neutrons. These radioactive isotopes are called radioisotopes .
Radiation can be emitted in different forms. There are three main types of radiation: alpha, beta and gamma radiation. These are shown in [link] , and are described below.
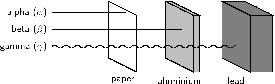
An alpha particle is made up of two protons and two neutrons bound together. This type of radiation has a positive charge . An alpha particle is sometimes represented using the chemical symbol , because it has the same structure as a Helium atom (two neutrons and two protons) ,but without the two electrons to balance the positive charge of the protons, hence the overall charge of +2. Alpha particles have a relatively low penetration power. Penetration power describes how easily the particles can pass through another material. Because alpha particles have a low penetration power, it means that even something as thin as a piece of paper, or the outside layer of the human skin, will absorb these particles so that they can't penetrate any further.
Alpha decay occurs in nuclei that contain too many protons, which results in strong repulsion forces between these positively charged particles. As a result of these repulsive forces, the nucleus emits an particle. This can be seen in the decay of Americium (Am) to Neptunium (Np).
Example:
Let's take a closer look at what has happened during this reaction. Americium (Z = 95; A = 241) undergoes decay and releases one alpha particle (i.e. 2 protons and 2 neutrons). The atom now has only 93 protons (Z = 93). On the periodic table, the element which has 93 protons (Z = 93) is called Neptunium. Therefore, the Americium atom has become a Neptunium atom. The atomic mass of the neptunium atom is 237 (A = 237) because 4 nucleons (2 protons and 2 neutrons) were emitted from the atom of Americium.
In nuclear physics, decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a particle (an electron or a positron) is emitted. In the case of electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus ( -), while in the case of a positron emission as beta plus ( +).
An electron and positron have identical physical characteristics except for opposite charge.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?