| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A particle moves in a straight line at a constant velocity of 30 m/s. What is its displacement between t = 0 and t = 5.0 s?
150 m
A particle moves in a straight line with an initial velocity of 30 m/s and a constant acceleration of 30 m/s 2 . If at and , what is the particle’s position at t = 5 s?
A particle moves in a straight line with an initial velocity of 30 m/s and constant acceleration 30 m/s 2 . (a) What is its displacement at t = 5 s? (b) What is its velocity at this same time?
a. 525 m;
b.
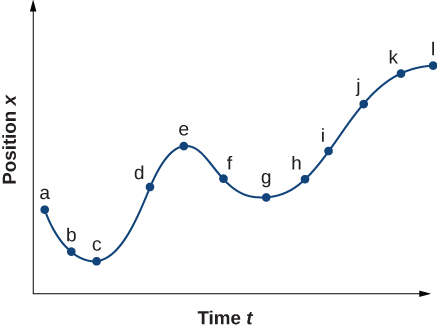
(a) Sketch a graph of velocity versus time corresponding to the graph of displacement versus time given in the following figure. (b) Identify the time or times ( t a , t b , t c , etc.) at which the instantaneous velocity has the greatest positive value. (c) At which times is it zero? (d) At which times is it negative?
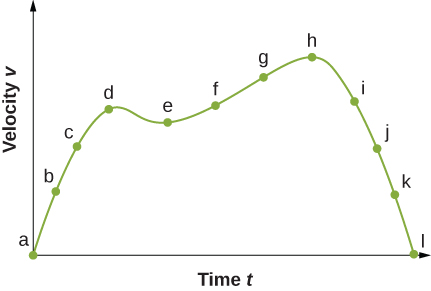
(a) Sketch a graph of acceleration versus time corresponding to the graph of velocity versus time given in the following figure. (b) Identify the time or times ( t a , t b , t c , etc.) at which the acceleration has the greatest positive value. (c) At which times is it zero? (d) At which times is it negative?
a.
b. The acceleration has the greatest positive value at
c. The acceleration is zero at
d. The acceleration is negative at
A particle has a constant acceleration of 6.0 m/s 2 . (a) If its initial velocity is 2.0 m/s, at what time is its displacement 5.0 m? (b) What is its velocity at that time?
At t = 10 s, a particle is moving from left to right with a speed of 5.0 m/s. At t = 20 s, the particle is moving right to left with a speed of 8.0 m/s. Assuming the particle’s acceleration is constant, determine (a) its acceleration, (b) its initial velocity, and (c) the instant when its velocity is zero.
a.
;
b.
;
c.
A well-thrown ball is caught in a well-padded mitt. If the acceleration of the ball is , and 1.85 ms elapses from the time the ball first touches the mitt until it stops, what is the initial velocity of the ball?
A bullet in a gun is accelerated from the firing chamber to the end of the barrel at an average rate of for . What is its muzzle velocity (that is, its final velocity)?
(a) A light-rail commuter train accelerates at a rate of 1.35 m/s 2 . How long does it take to reach its top speed of 80.0 km/h, starting from rest? (b) The same train ordinarily decelerates at a rate of 1.65 m/s 2 . How long does it take to come to a stop from its top speed? (c) In emergencies, the train can decelerate more rapidly, coming to rest from 80.0 km/h in 8.30 s. What is its emergency acceleration in meters per second squared?
While entering a freeway, a car accelerates from rest at a rate of 2.04 m/s 2 for 12.0 s. (a) Draw a sketch of the situation. (b) List the knowns in this problem. (c) How far does the car travel in those 12.0 s? To solve this part, first identify the unknown, then indicate how you chose the appropriate equation to solve for it. After choosing the equation, show your steps in solving for the unknown, check your units, and discuss whether the answer is reasonable. (d) What is the car’s final velocity? Solve for this unknown in the same manner as in (c), showing all steps explicitly.
a.

b. Knowns:
, and
;
c.
, the answer seems reasonable at about 172.8 m; d.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?