| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Like linear momentum, angular momentum is the measure of the "quantity of motion". From Newton's second law, we know that first time derivative of linear momentum gives net external force on a particle. By analogy, we expect that this quantity (angular momentum) should have an expression such that its first time derivative yields torque on the particle.
Angular momentum is associated with a particle in motion. The motion need not be rotational motion, but any motion. Importantly, it is measured with respect to a fixed point.
Angular momentum of a particle about a point is defined as a vector, denoted as " ℓ ".
where " r " is the linear vector connecting the position of the particle with the "point" about which angular momentum is measured and " p " is the linear momentum vector. In case, the point coincides with the origin of coordinate system, the vector " r " becomes the position vector.
We should note here that small letter "ℓ" is used to denote angular momentum of a particle. The corresponding capital letter "L" is reserved for angular momentum of a system of particle or rigid body. This convention helps to distinguish the context and may be adhered to.
The SI unit of angular momentum is , which is equivalent to J-s.
Like in the case of torque, the magnitude of angular momentum can be obtained using any of the following relations :
Angular momentum of a particle
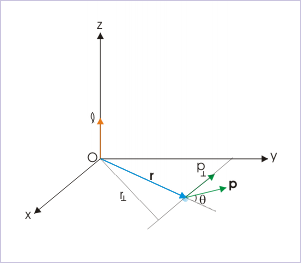
1: Angular momentum in terms of angle enclosed
2: Angular momentum in terms of force perpendicular to position vector
3: Angular momentum in terms of moment arm
If the particle is moving with a velocity " v ", then the expression of angular momentum becomes :
Again, we can interpret this vector product as in the case of torque. Its magnitude can be obtained using any of the following relations :
Problem : A particle of mass, "m", moves with a constant velocity "v" along a straight line parallel to x-axis as shown in the figure. Find the angular momentum of the particle about the origin of the coordinate system. Also discuss the nature of angular momentum in this case.
Angular momentum of a particle
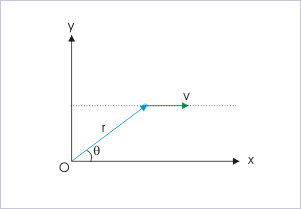
Solution : The magnitude of the angular momentum is given by :
This expression can be rearranged as :
From the ΔOAC, it is clear that :
Angular momentum of a particle
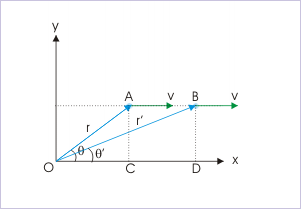
At another instant, we have :
But the perpendicular distance between two parallel lines are same (AC = BD). Thus,
Also, the quantities "m" and "v" are constants. Therefore, angular momentum of the moving particle about origin "O" is a constant.
Since angular momentum is constant, its rate of change with time is zero. But, time rate of change of angular momentum is equal to torque (we shall develop this relation in next module). It means that torque on the particle is zero as time derivate of a constant is zero. Indeed it should be so as the particle is not accelerated. This result underlines the fact that the concept of angular momentum is consistent even for the description of linear motion as set out in the beginning of this module.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?