| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Questions and their answers are presented here in the module text format as if it were an extension of the theoretical treatment of the topic. The idea is to provide a verbose explanation of the solution, detailing the application of theory. Solution presented here, therefore, is treated as the part of the understanding process – not merely a Q/A session. The emphasis is to enforce ideas and concepts, which can not be completely absorbed unless they are put to real time situation.
We discuss problems, whose analysis is suited to the technique of treating rolling motion as pure rotation. For this reason, questions are categorized in terms of the characterizing features pertaining to the questions :
Example 1
Problem : At an instant, the contact point of a rolling disk of radius “R” coincides with the origin of the coordinate system. If the disk rolls with constant angular velocity, “ω”, along a straight line, then find the position of a particle on the vertical diameter, whose velocity is 1/ 2 of the velocity with which the disk rolls.
Solution : Here, the particle on the vertical diameter moves with a velocity, which is 1/ 2 of that of the velocity of the center of mass. Now, velocity of center of mass is :
Let the particle be at a distance “y” from the point of contact on the vertical diameter. Then, velocity of the particle is :
Velocity of a particle
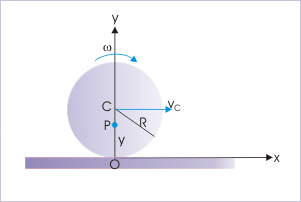
According to question,
Putting values,
Example 2
Problem : At an instant, the contact point of a rolling disk of radius “R” coincides with the origin of the coordinate system. If the disk rolls with constant angular velocity, “ω”, along a straight line, then find the position of a particle on the rim of the disk, whose speed is same as the speed with which the disk rolls.
Solution : Here, the particle on the rim of the disk moves with the same velocity as that of the velocity of the center of mass. Now, velocity of center of mass is :
Let the particle be at P(x,y) as shown in the figure. Then, velocity of the particle is :
Velocity of a particle
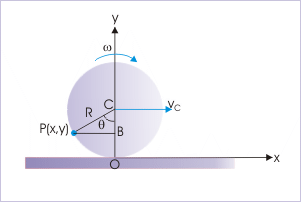
According to question,
Putting values,
Since there are two such points on the rim on either side of the vertical line, the coordinates of the positions of the particles, having same speed as that of center of mass are :
Example 3

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?