| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Questions and their answers are presented here in the module text format as if it were an extension of the theoretical treatment of the topic. The idea is to provide a verbose explanation of the solution, detailing the application of theory. Solution presented here, therefore, is treated as the part of the understanding process – not merely a Q/A session. The emphasis is to enforce ideas and concepts, which can not be completely absorbed unless they are put to real time situation.
We discuss problems, which highlight certain aspects of the rolling motion. For this reason, questions are categorized in terms of the characterizing features pertaining to the questions :
Example 1
Problem : What is the speed of center of mass, if a solid sphere of radius 30 cm rolls at 2 revolutions per second along a straight line?
Solution : The particle on the outer surface in contact with the surface moves the same distance in rotation as the center of mass moves in translation. In 1 second, the particle on the rim moves a distance :
Alternatively, we can find the speed of the center of mass, using equation of rolling as :
Example 2
Problem : A disk of radius “R” is rolling with an angular speed of “ω”. If the center of mass at time t = 0 coincides with the origin of the coordinate system, then find the velocity of the point 0,r (r<R).
Solution : The position of the point is shown in the figure. It lies on the y-axis. The linear velocity of the center of mass is :
Pure rolling of a disk
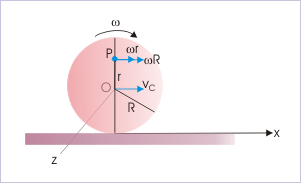
The component of velocity due to pure translation, therefore, is :
On the other hand, linear velocity of the point due to pure rotation is tangential to the circle drawn with radius “r”,
Hence, velocity of the point is :
This question highlights an important fact that velocity due to pure translations is constant for all particles in the rolling body. On the other hand, linear velocities of the particles due to rotation vary, depending upon their relative positions (" r ") with respect to COM. The resultant velocities of particles, therefore, vary as a whole depending on their positions in the body.
Example 3
Problem : A person rolls a cylinder by pushing a board on top of the cylinder horizontally. The board does not slide and cylinder rolls without sliding. If the linear distance moved by the person is “L”, then find (i) the length of board that rolls over the top of the cylinder and (ii) linear distance covered by cylinder.
Pure rolling of a cylinder
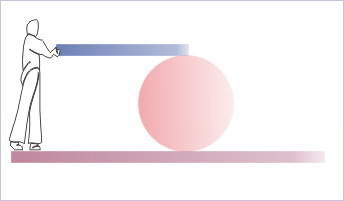
Solution : The person needs to move a distance, which is sum of the length of board pushed over and the linear distance moved by the central axis of the cylinder in horizontal direction. This is the requirement of physical situation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?