| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
While basking in the warmth of the summer sun, a student reads of the latest breakthrough in achieving sustained thermonuclear power and vaguely recalls hearing about the cold fusion controversy. The three are connected. The Sun's energy is produced by nuclear fusion (see [link] ). Thermonuclear power is the name given to the use of controlled nuclear fusion as an energy source. While research in the area of thermonuclear power is progressing, high temperatures and containment difficulties remain. The cold fusion controversy centered around unsubstantiated claims of practical fusion power at room temperatures.

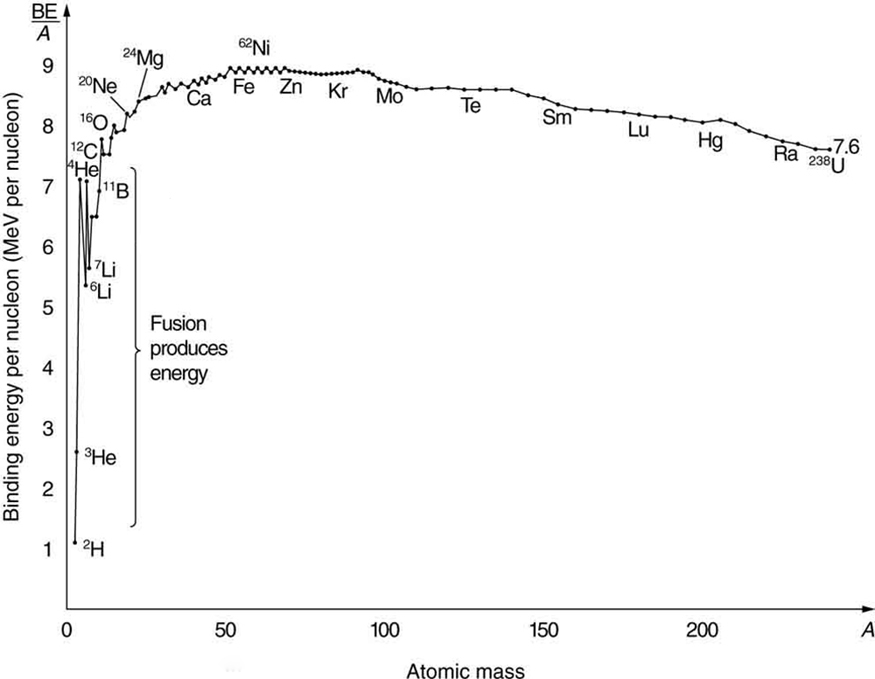
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two nuclei are combined, or fused , to form a larger nucleus. We know that all nuclei have less mass than the sum of the masses of the protons and neutrons that form them. The missing mass times equals the binding energy of the nucleus—the greater the binding energy, the greater the missing mass. We also know that , the binding energy per nucleon, is greater for medium-mass nuclei and has a maximum at Fe (iron). This means that if two low-mass nuclei can be fused together to form a larger nucleus, energy can be released. The larger nucleus has a greater binding energy and less mass per nucleon than the two that combined. Thus mass is destroyed in the fusion reaction, and energy is released (see [link] ). On average, fusion of low-mass nuclei releases energy, but the details depend on the actual nuclides involved.
The major obstruction to fusion is the Coulomb repulsion between nuclei. Since the attractive nuclear force that can fuse nuclei together is short ranged, the repulsion of like positive charges must be overcome to get nuclei close enough to induce fusion. [link] shows an approximate graph of the potential energy between two nuclei as a function of the distance between their centers. The graph is analogous to a hill with a well in its center. A ball rolled from the right must have enough kinetic energy to get over the hump before it falls into the deeper well with a net gain in energy. So it is with fusion. If the nuclei are given enough kinetic energy to overcome the electric potential energy due to repulsion, then they can combine, release energy, and fall into a deep well. One way to accomplish this is to heat fusion fuel to high temperatures so that the kinetic energy of thermal motion is sufficient to get the nuclei together.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?