| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Attempts to unify the four basic forces are discussed in relation to elementary particles later in this text. By “unify” we mean finding connections between the forces that show that they are different manifestations of a single force. Even if such unification is achieved, the forces will retain their separate characteristics on the macroscopic scale and may be identical only under extreme conditions such as those existing in the early universe.
Physicists are now exploring whether the four basic forces are in some way related. Attempts to unify all forces into one come under the rubric of Grand Unified Theories (GUTs), with which there has been some success in recent years. It is now known that under conditions of extremely high density and temperature, such as existed in the early universe, the electromagnetic and weak nuclear forces are indistinguishable. They can now be considered to be different manifestations of one force, called the electroweak force. So the list of four has been reduced in a sense to only three. Further progress in unifying all forces is proving difficult—especially the inclusion of the gravitational force, which has the special characteristics of affecting the space and time in which the other forces exist.
While the unification of forces will not affect how we discuss forces in this text, it is fascinating that such underlying simplicity exists in the face of the overt complexity of the universe. There is no reason that nature must be simple—it simply is.
All forces act at a distance. This is obvious for the gravitational force. Earth and the Moon, for example, interact without coming into contact. It is also true for all other forces. Friction, for example, is an electromagnetic force between atoms that may not actually touch. What is it that carries forces between objects? One way to answer this question is to imagine that a force field surrounds whatever object creates the force. A second object (often called a test object ) placed in this field will experience a force that is a function of location and other variables. The field itself is the “thing” that carries the force from one object to another. The field is defined so as to be a characteristic of the object creating it; the field does not depend on the test object placed in it. Earth’s gravitational field, for example, is a function of the mass of Earth and the distance from its center, independent of the presence of other masses. The concept of a field is useful because equations can be written for force fields surrounding objects (for gravity, this yields at Earth’s surface), and motions can be calculated from these equations. (See [link] .)
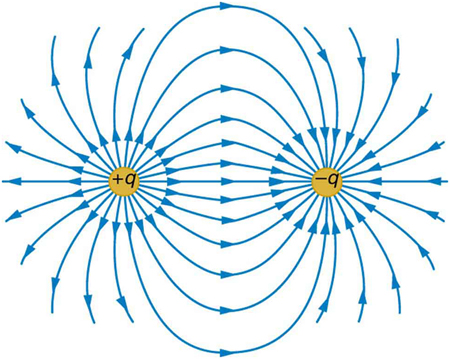
The concept of a force field is also used in connection with electric charge and is presented in Electric Charge and Electric Field . It is also a useful idea for all the basic forces, as will be seen in Particle Physics . Fields help us to visualize forces and how they are transmitted, as well as to describe them with precision and to link forces with subatomic carrier particles.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?