| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Magnetism is a force that certain kinds of objects, which are called `magnetic' objects, can exert on each other without physically touching. A magnetic object is surrounded by a magnetic `field' that gets weaker as one moves further away from the object. A second object can feel a magnetic force from the first object because it feels the magnetic field of the first object.
Humans have known about magnetism for many thousands of years. For example, lodestone is a magnetised form of the iron oxide mineral magnetite . It has the property of attracting iron objects. It is referred to in old European and Asian historicalrecords; from around 800 BCE in Europe and around 2 600 BCE in Asia.
The root of the English word magnet is from the Greek word magnes , probably from Magnesia in Asia Minor, once an important source of lodestone.
A magnetic field is a region in space where a magnet or object made of magnetic material will experience a non-contact force.
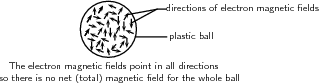
Electrons inside any object have magnetic fields associated with them. In most materials these fields point in alldirections, so the net magnetic field is zero. For example, in the plastic ball below, the directions of the magnetic fields of the electrons (shown by the arrows) are pointingin different directions and cancel each other out. Therefore the plastic ball is not magnetic and has no magnetic field.
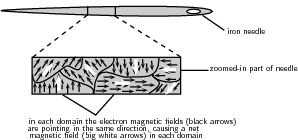
In some materials (e.g. iron), called ferromagnetic materials, there are regions called domains , where the electrons' magnetic fields line up with each other. All the atoms in each domain are grouped together so that the magnetic fields from their electrons point the same way. The picture shows a piece of an iron needle zoomed in to show the domains with the electric fields lined up inside them.
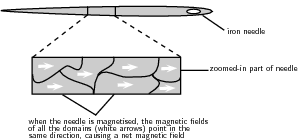
In permanent magnets, many domains are lined up, resulting in a net magnetic field . Objects made from ferromagnetic materials can be magnetised, for example by rubbing a magnetalong the object in one direction. This causes the magnetic fields of most, or all, of the domains to line up in one direction. As a result the object as a whole will have a net magnetic field. It is magnetic . Once a ferromagnetic object has been magnetised, it can stay magnetic without another magnet being nearby (i.e. without being in another magnetic field). In the picture below, the needle has been magnetised because the magnetic fields in all the domains are pointing in the same direction.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?