| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
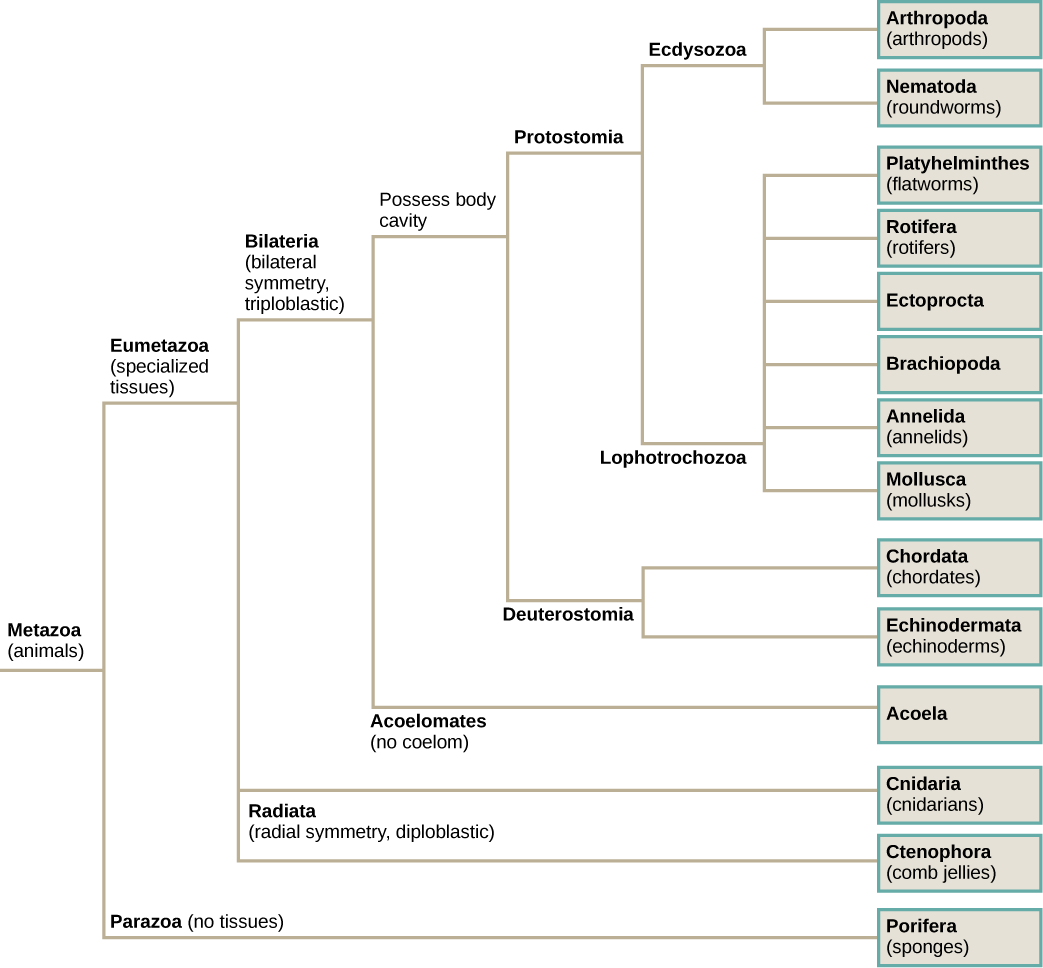
Scientists have developed a classification scheme that categorizes all members of the animal kingdom, although there are exceptions to most “rules” governing animal classification ( [link] ). Animals are primarily classified according to morphological and developmental characteristics, such as a body plan. One of the most prominent features of the body plan of true animals is that they are morphologically symmetrical. This means that their distribution of body parts is balanced along an axis. Additional characteristics include the number of tissue layers formed during development, the presence or absence of an internal body cavity, and other features of embryological development, such as the origin of the mouth and anus.
Which of the following statements is false?
At a very basic level of classification, true animals can be largely divided into three groups based on the type of symmetry of their body plan: radially symmetrical, bilaterally symmetrical, and asymmetrical. Asymmetry is a unique feature of Parazoa ( [link] a ). Only a few animal groups display radial symmetry. All types of symmetry are well suited to meet the unique demands of a particular animal’s lifestyle.
Radial symmetry is the arrangement of body parts around a central axis, as is seen in a drinking glass or pie. It results in animals having top and bottom surfaces but no left and right sides, or front or back. The two halves of a radially symmetrical animal may be described as the side with a mouth or “oral side,” and the side without a mouth (the “aboral side”). This form of symmetry marks the body plans of animals in the phyla Ctenophora and Cnidaria, including jellyfish and adult sea anemones ( [link] bc ). Radial symmetry equips these sea creatures (which may be sedentary or only capable of slow movement or floating) to experience the environment equally from all directions.

Bilateral symmetry involves the division of the animal through a sagittal plane, resulting in two mirror image, right and left halves, such as those of a butterfly ( [link] d ), crab, or human body. Animals with bilateral symmetry have a “head” and “tail” (anterior vs. posterior), front and back (dorsal vs. ventral), and right and left sides ( [link] ). All true animals except those with radial symmetry are bilaterally symmetrical. The evolution of bilateral symmetry that allowed for the formation of anterior and posterior (head and tail) ends promoted a phenomenon called cephalization, which refers to the collection of an organized nervous system at the animal’s anterior end. In contrast to radial symmetry, which is best suited for stationary or limited-motion lifestyles, bilateral symmetry allows for streamlined and directional motion. In evolutionary terms, this simple form of symmetry promoted active mobility and increased sophistication of resource-seeking and predator-prey relationships.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-nya-05 - general biology i' conversation and receive update notifications?