| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In some circumstances, a lens forms an obvious image, such as when a movie projector casts an image onto a screen. In other cases, the image is less obvious. Where, for example, is the image formed by eyeglasses? We will use ray tracing for thin lenses to illustrate how they form images, and we will develop equations to describe the image formation quantitatively.
Consider an object some distance away from a converging lens, as shown in [link] . To find the location and size of the image formed, we trace the paths of selected light rays originating from one point on the object, in this case the top of the person’s head. The figure shows three rays from the top of the object that can be traced using the ray tracing rules given above. (Rays leave this point going in many directions, but we concentrate on only a few with paths that are easy to trace.) The first ray is one that enters the lens parallel to its axis and passes through the focal point on the other side (rule 1). The second ray passes through the center of the lens without changing direction (rule 3). The third ray passes through the nearer focal point on its way into the lens and leaves the lens parallel to its axis (rule 4). The three rays cross at the same point on the other side of the lens. The image of the top of the person’s head is located at this point. All rays that come from the same point on the top of the person’s head are refracted in such a way as to cross at the point shown. Rays from another point on the object, such as her belt buckle, will also cross at another common point, forming a complete image, as shown. Although three rays are traced in [link] , only two are necessary to locate the image. It is best to trace rays for which there are simple ray tracing rules. Before applying ray tracing to other situations, let us consider the example shown in [link] in more detail.
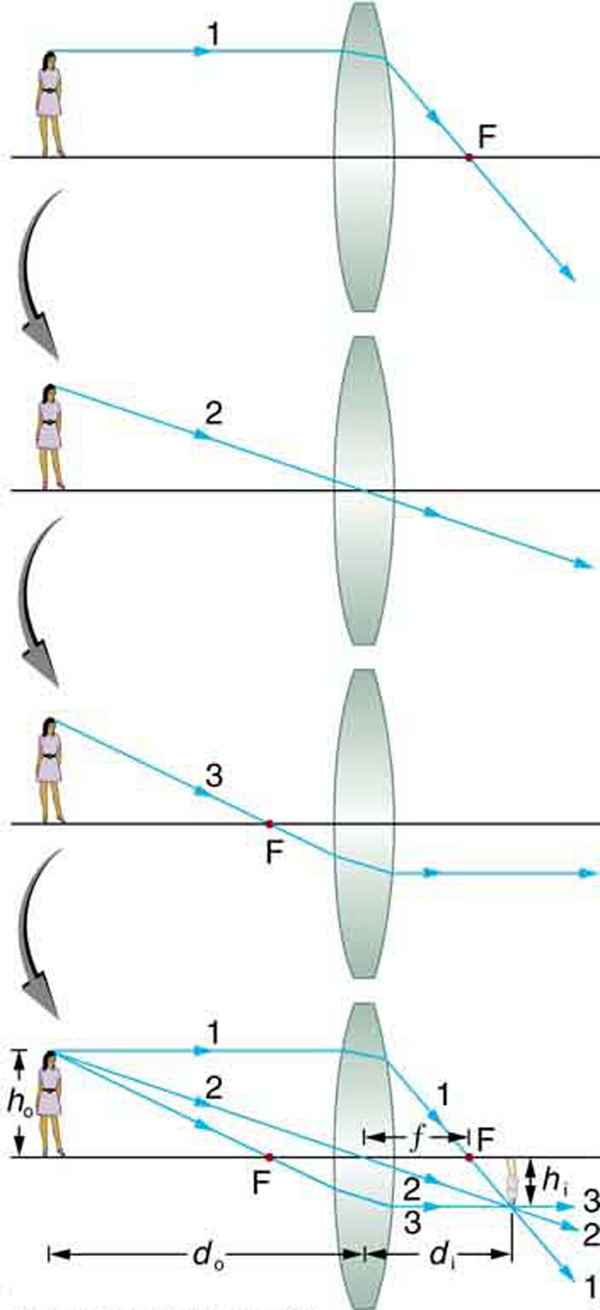
The image formed in [link] is a real image , meaning that it can be projected. That is, light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the image and can be projected onto a screen, a piece of film, or the retina of an eye, for example. [link] shows how such an image would be projected onto film by a camera lens. This figure also shows how a real image is projected onto the retina by the lens of an eye. Note that the image is there whether it is projected onto a screen or not.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General physics ii phy2202ca' conversation and receive update notifications?